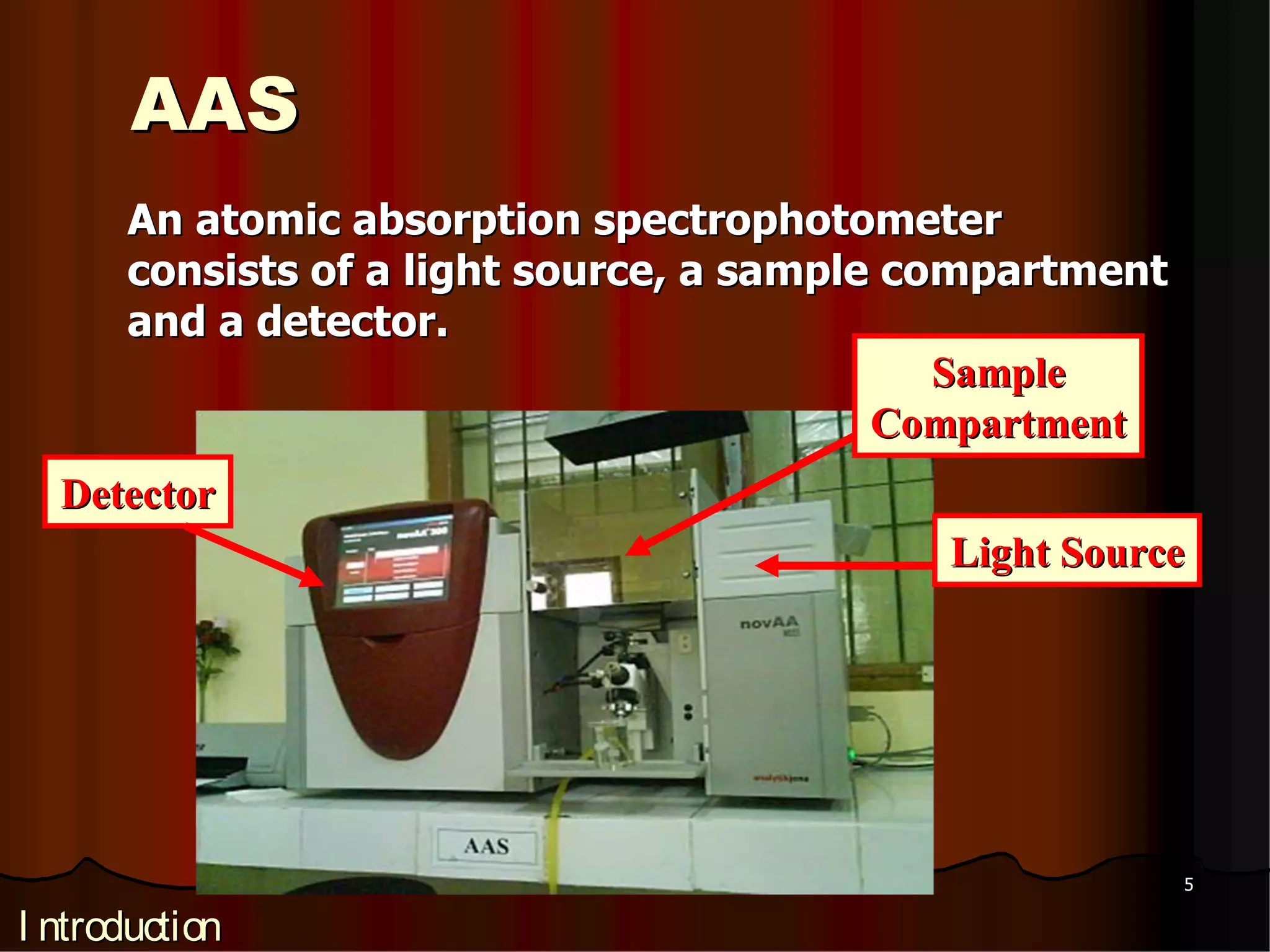
1. Atomic absorption spectroscopy is a quantitative analytical technique used to determine the concentration of metals and some nonmetals in solutions. It works by measuring the absorption of light by ground state atoms at their characteristic resonance wavelengths.
2. The technique involves atomizing the sample using a flame or electrothermal heating and passing the gaseous atoms through a beam of resonance wavelength light from a hollow cathode lamp. The amount of light absorbed is proportional to the number of atoms in the ground state.
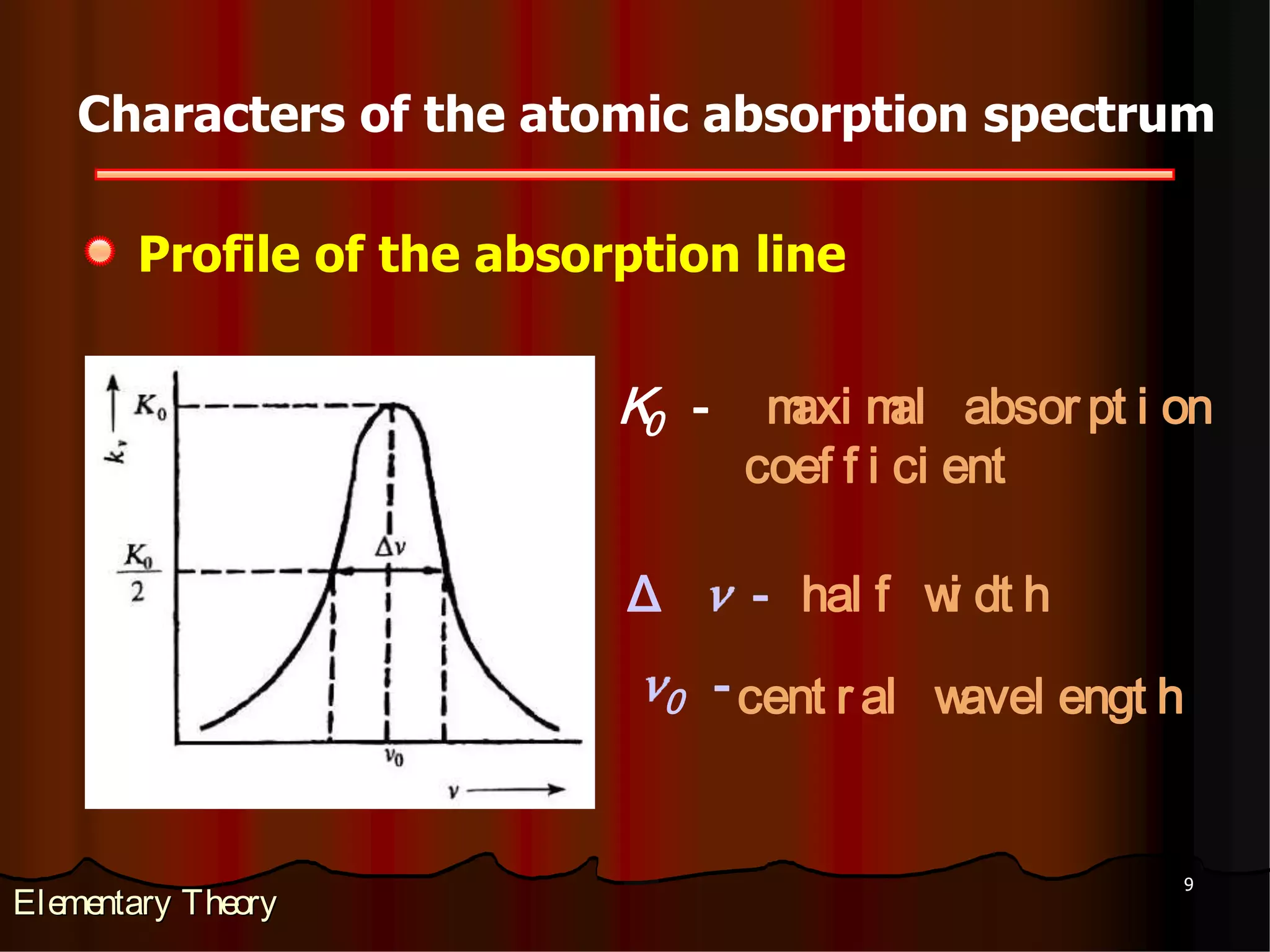
3. Interferences can occur from spectral overlap, molecular absorption, light scattering, chemical interactions that form non-volatile compounds, and physical properties affecting atomization efficiency. Various methods such as changing operating parameters, adding chemical modifiers,



































![Hydride generation methods
For arsenic (As), antimony (Te) and selenium (Se)
NaBH4 heat
As (V) AsH3 As0(gas) + H2
[H+] in flame
(sol)
38
I nstrumentation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atomicabsorptionspectroscopy-121216073441-phpapp01/75/Atomic-absorption-spectroscopy-38-2048.jpg)

















![Advantages and disadvantages
High sensitivity
[10-10g (flame), 10-14g (non-flame)]
Good accuracy
(Relative error 0.1 ~ 0.5 % )
High selectivity
Widely used
A resonance line source is required for
each element to be determined
57](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atomicabsorptionspectroscopy-121216073441-phpapp01/75/Atomic-absorption-spectroscopy-56-2048.jpg)