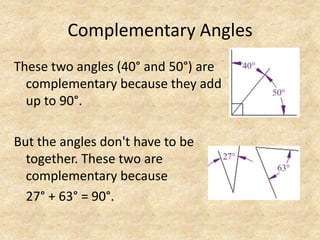
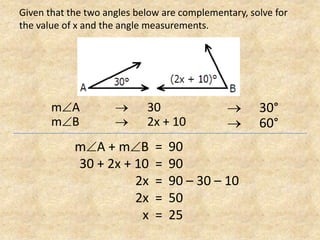
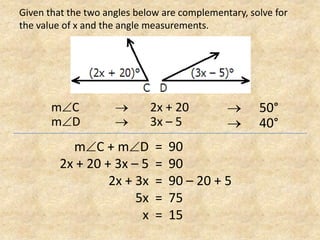
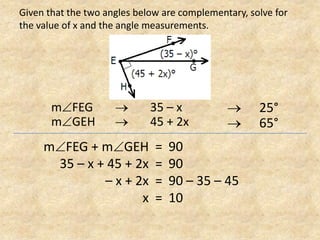
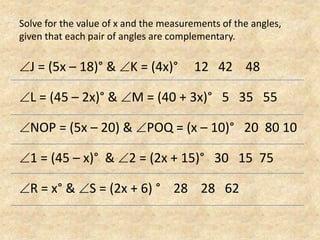
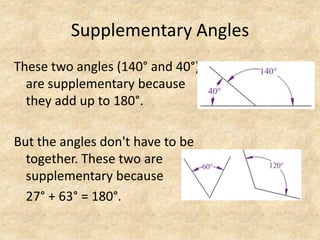
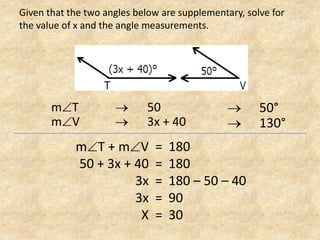
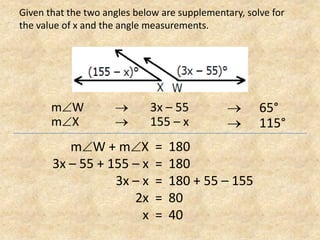
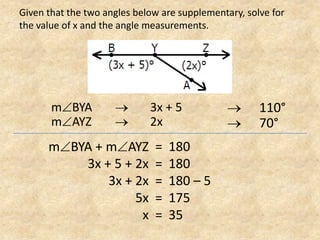
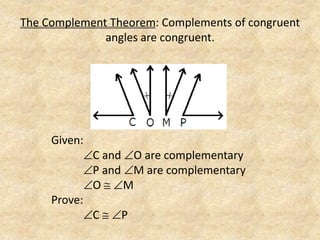
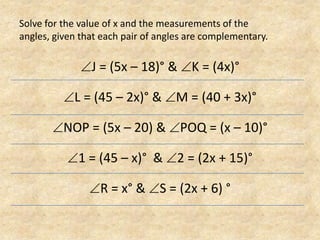The document defines and provides examples of complementary angles, supplementary angles, linear pairs, and vertical angles. It also states the Complement Theorem, Supplement Theorem, Linear Pair Postulate, and Vertical Angle Theorem. Several word problems are included where the value of x and angle measurements are solved for given complementary, supplementary, or congruent angle relationships.