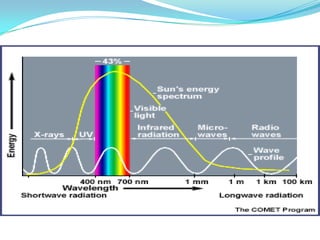
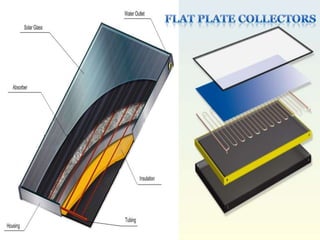
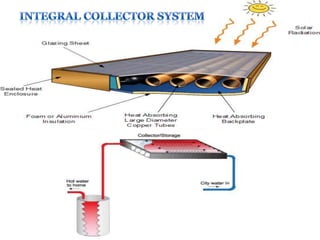
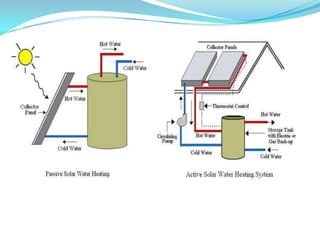
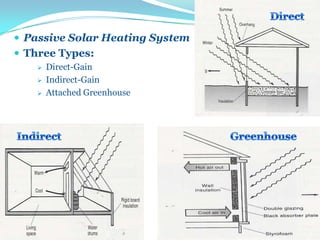
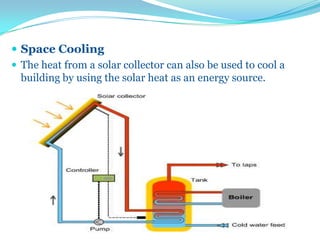
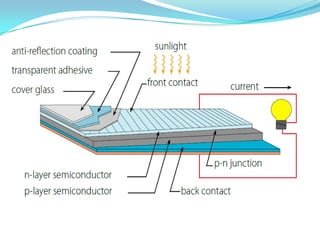
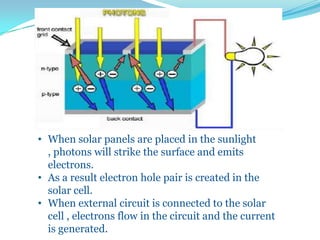
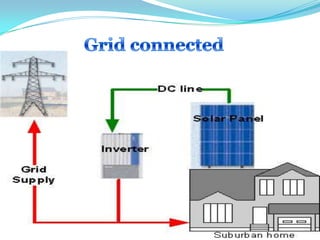
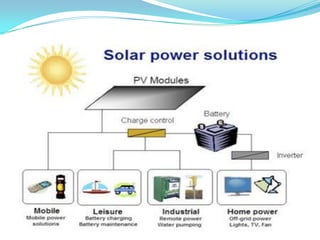
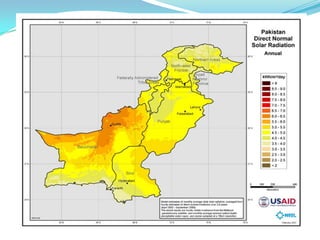
This document provides an overview of solar energy. It discusses that solar energy originates from thermonuclear fusion in the sun and consists of radiant light and heat. It also discusses different types of solar radiation and how solar energy can be used for heating, cooling, and generating electricity through solar thermal technologies and photovoltaic cells. The document also discusses current and future prospects of solar power development in Pakistan.