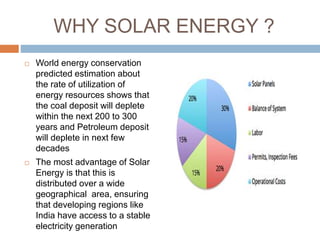
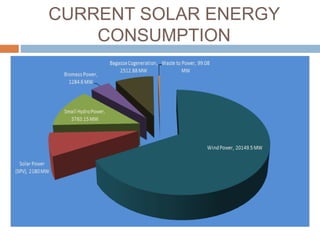
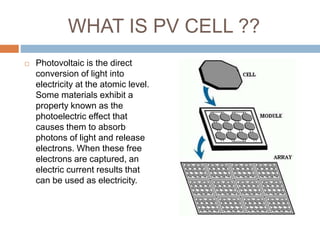
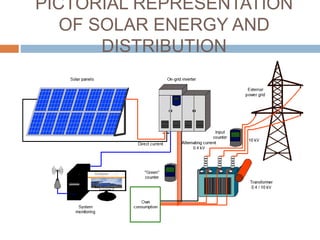
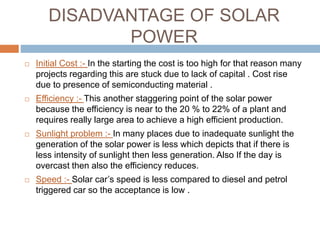
Solar energy comes in two forms: thermal and electric. Thermal solar energy is heat from the sun, while electric solar energy is produced directly from sunlight using photovoltaic cells. Solar energy is a renewable resource that is distributed widely on Earth and can help meet growing energy needs as fossil fuel reserves are depleted. However, solar power systems are expensive to install initially and have lower efficiencies than other energy sources. Further technological advances are needed to improve solar energy's cost-effectiveness and ability to meet global energy demands.