Embed presentation
Download to read offline


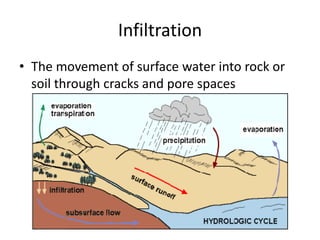





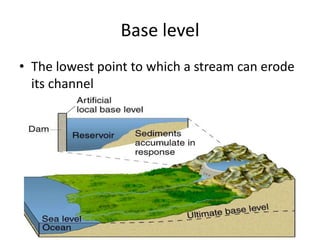





The document discusses key concepts about running water and the water cycle. It defines terms like infiltration, transpiration, gradient, stream channel, discharge, tributary, base level, and meander. It explains that water constantly circulates among the oceans, atmosphere, geosphere, and biosphere in the water cycle. Balance in the cycle means annual precipitation equals evaporation globally. A stream's ability to erode and transport materials depends on its velocity, while gradient decreases and discharge increases from headwaters to the mouth.













