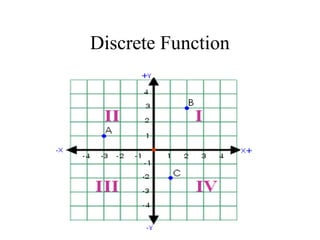
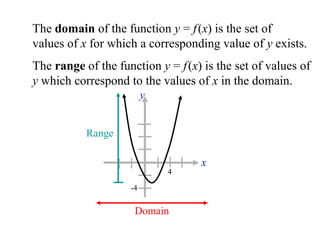
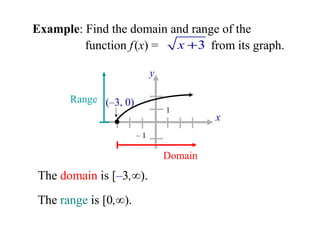
The document discusses domain and range for functions. It defines discrete and continuous functions. A discrete function has points that are not connected, while a continuous function forms a smooth, unbroken line or curve. Examples are given of determining the domain and range from graphs of continuous functions. The domain is the set of x-values for which there is a corresponding y-value. The range is the set of y-values. Homework problems on finding domain and range are assigned.








![Example 2
Domain
(−∞, ∞)
Range
(−∞, 4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1day8continuousfunctionsdomainrange-131106134605-phpapp01/85/Unit-1-day-8-continuous-functions-domain-range-12-320.jpg)

![6
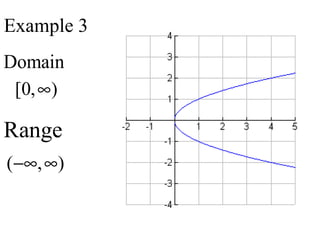
Domain
(−∞,3]
4
Range
[1, ∞)
2
-5
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1day8continuousfunctionsdomainrange-131106134605-phpapp01/85/Unit-1-day-8-continuous-functions-domain-range-15-320.jpg)
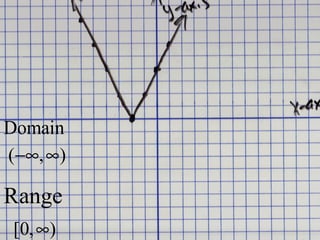

![Domain
(−∞, −1) U [1, 6]
Range
(−∞, 6)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1day8continuousfunctionsdomainrange-131106134605-phpapp01/85/Unit-1-day-8-continuous-functions-domain-range-18-320.jpg)
