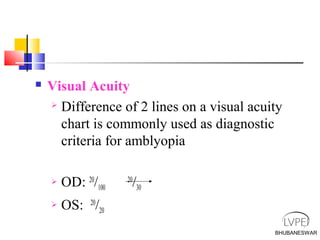
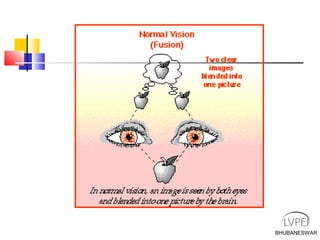
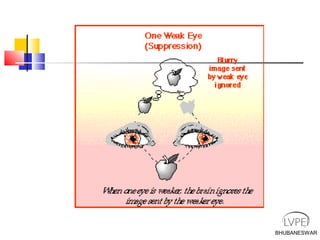
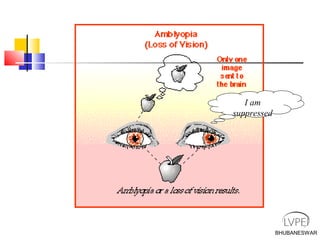
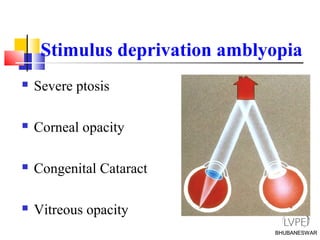
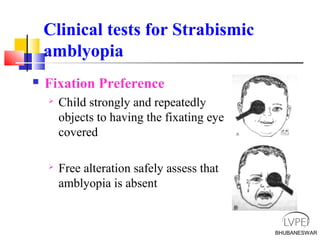
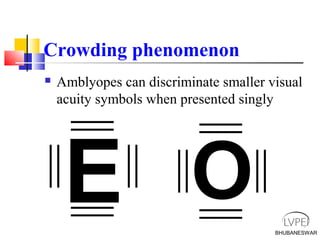
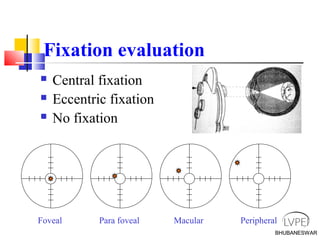
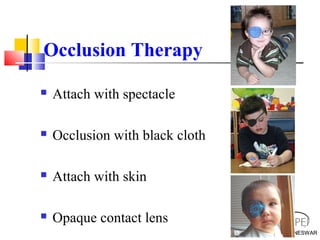
Amblyopia, commonly known as lazy eye, is a condition where vision is reduced in one or both eyes and cannot be corrected by glasses or contact lenses. It is caused by abnormal visual development during childhood. There are several types of amblyopia including stimulus deprivation, strabismic, anisometric, and isometric amblyopia. Treatment involves patching or blurring the stronger eye to encourage use of the weaker eye, along with refractive correction if needed. Therapy is most effective when started early in childhood.