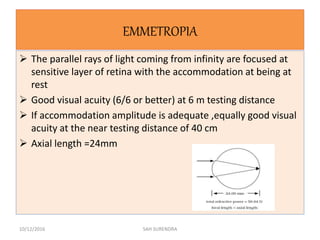
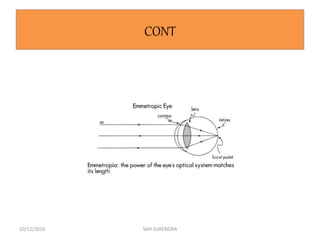
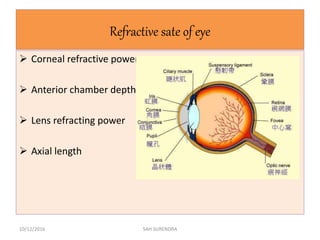
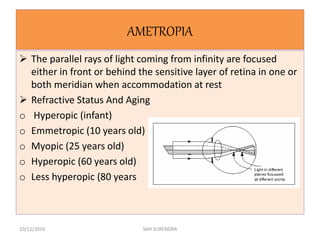
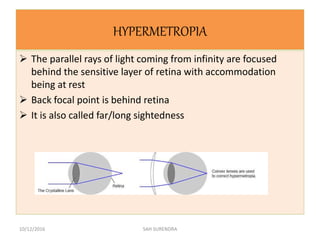
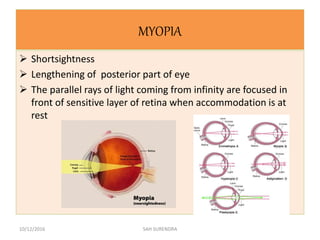
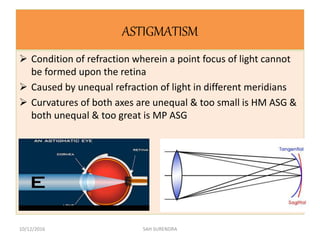
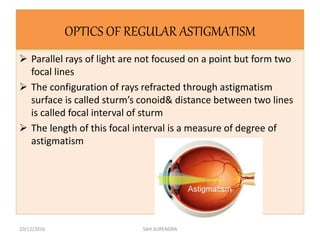
This document provides an overview of refractive errors, including emmetropia, ametropia, and various types of refractive errors such as hyperopia, myopia, astigmatism, aphakia, and pseudophakia. It discusses the optical conditions and clinical features of each type of refractive error, as well as their causes, treatment options, and potential complications. Key information covered includes the definition of emmetropia as the eye's ability to focus light correctly on the retina, the various causes and classifications of refractive errors, and management approaches for different refractive conditions including optical corrections and refractive surgery.