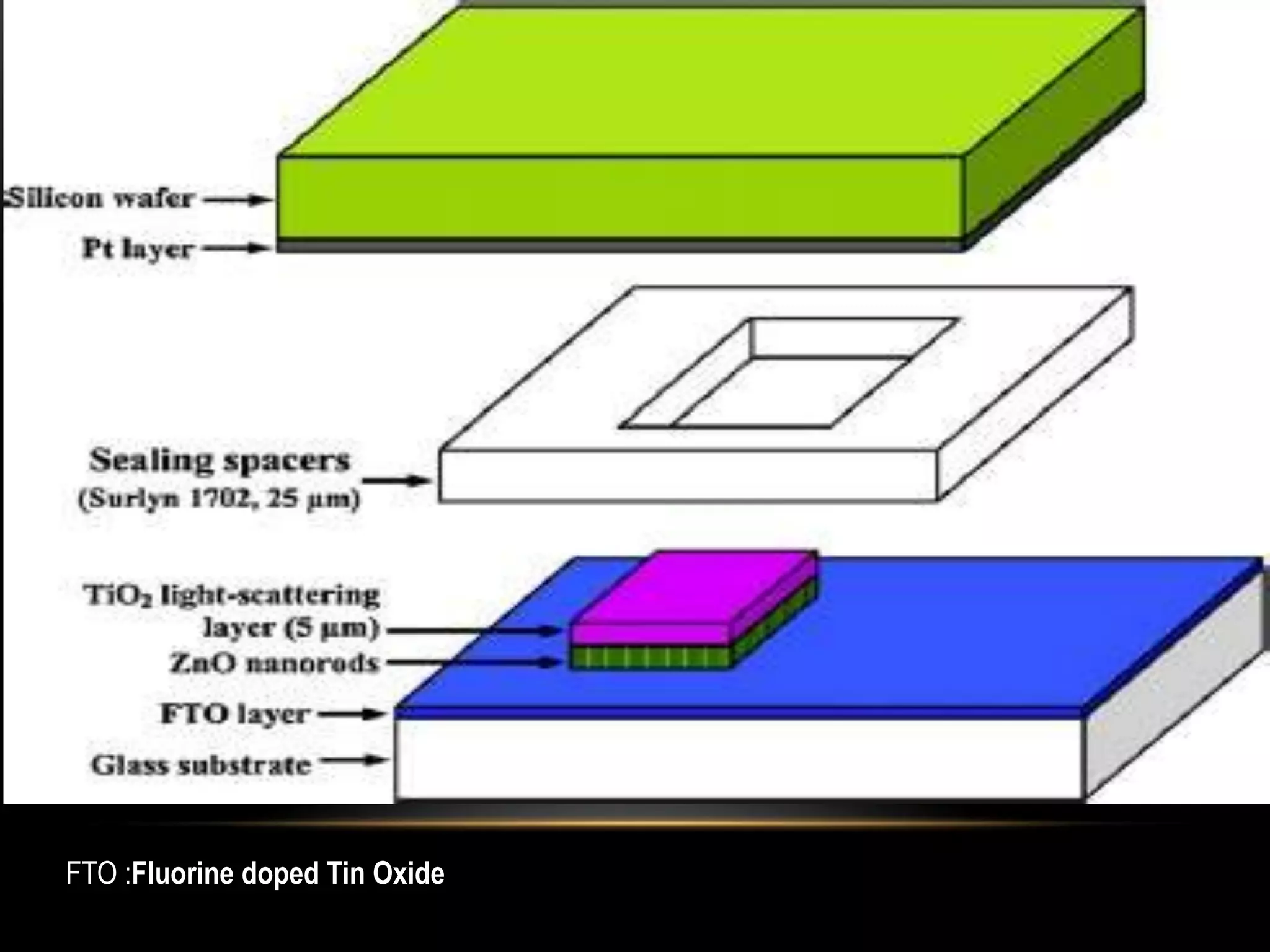
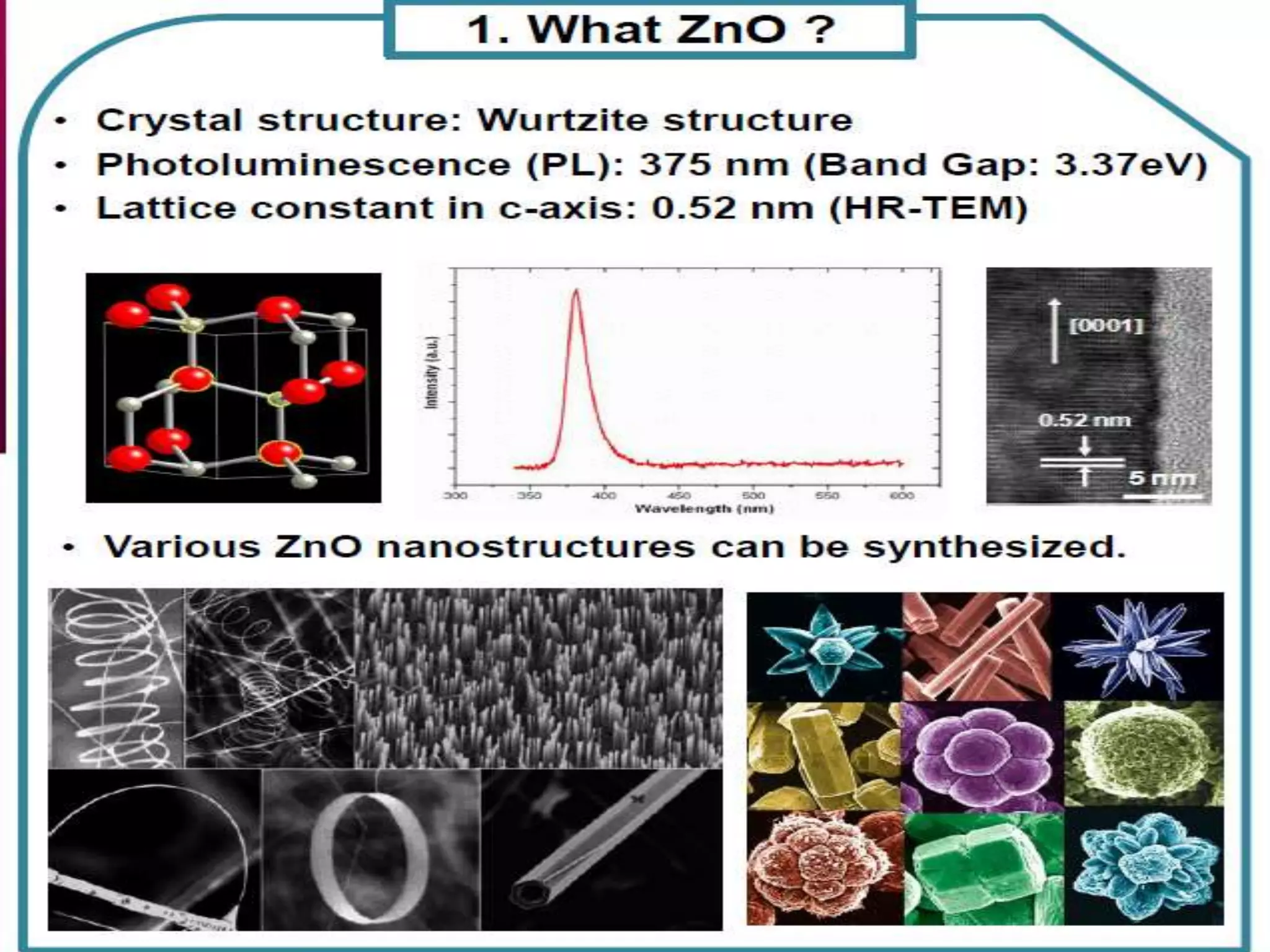
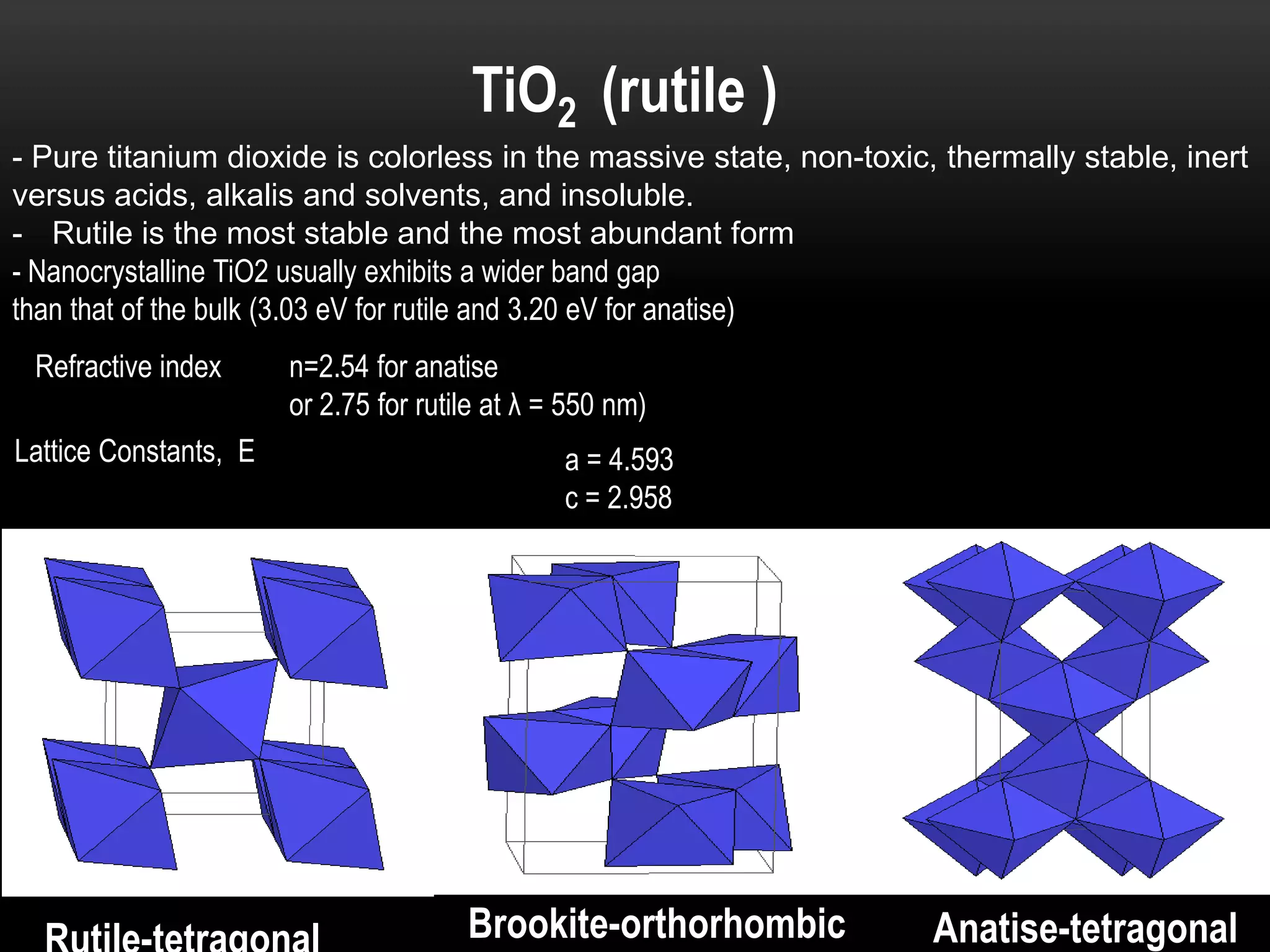
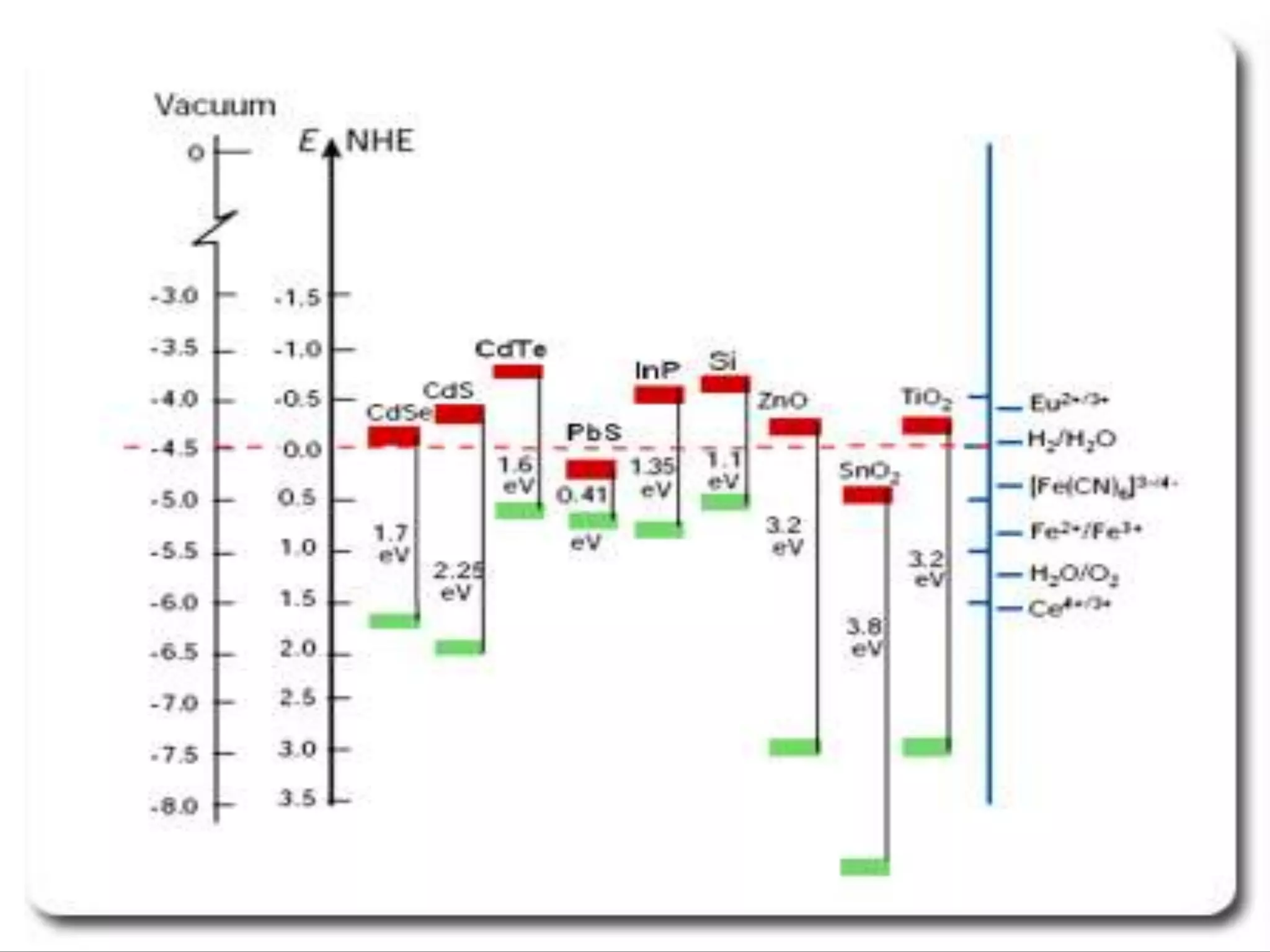
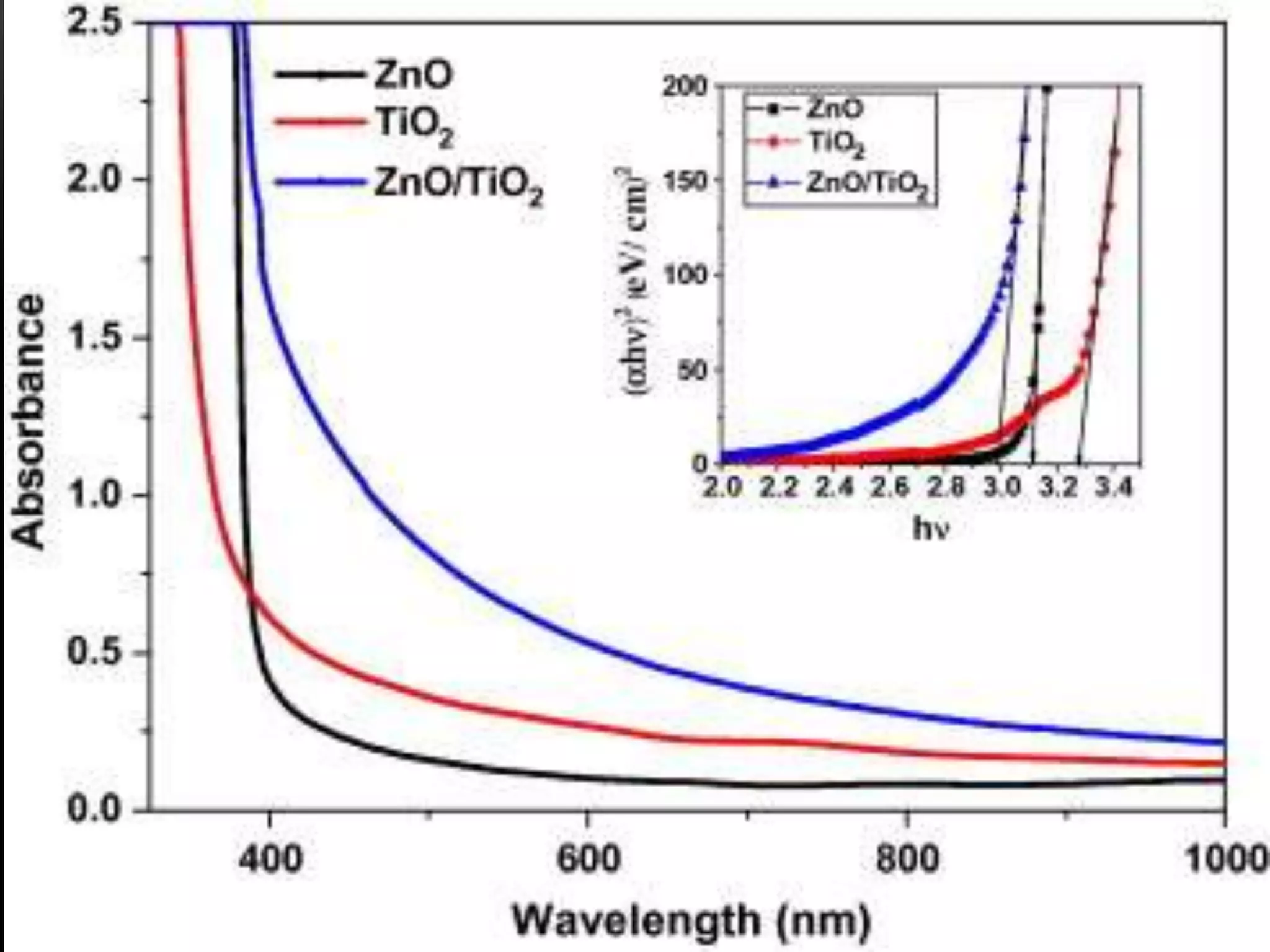
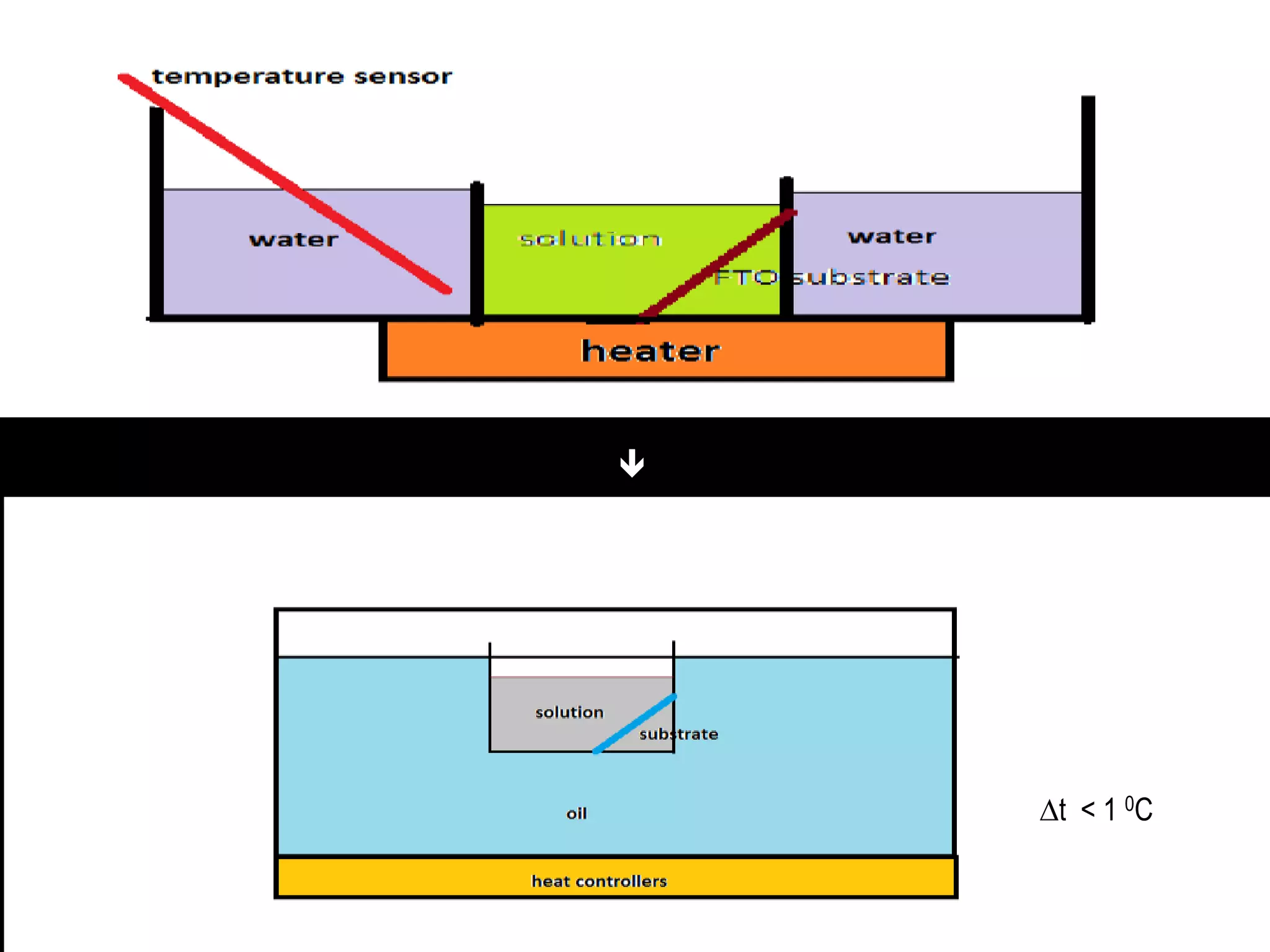
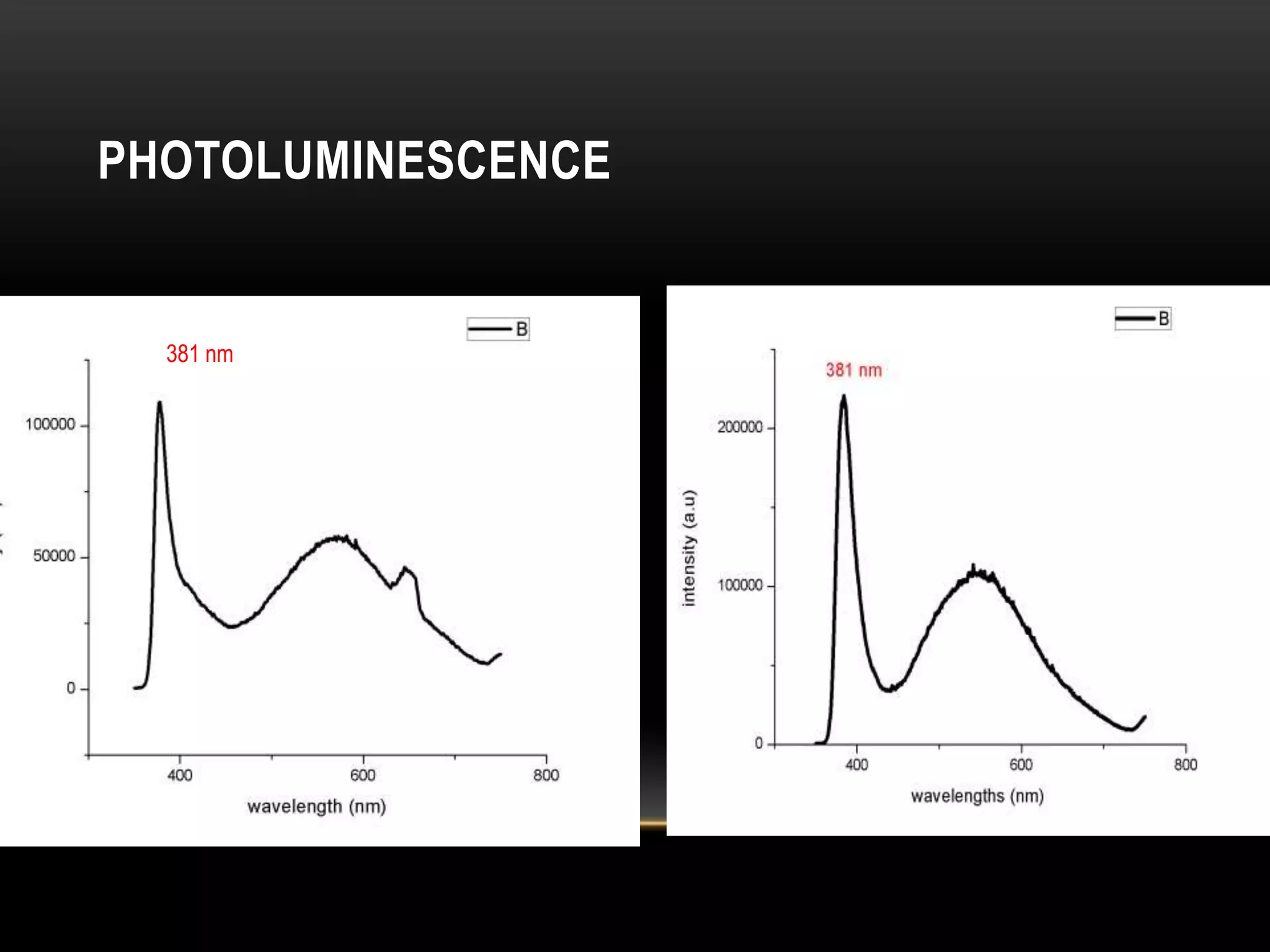
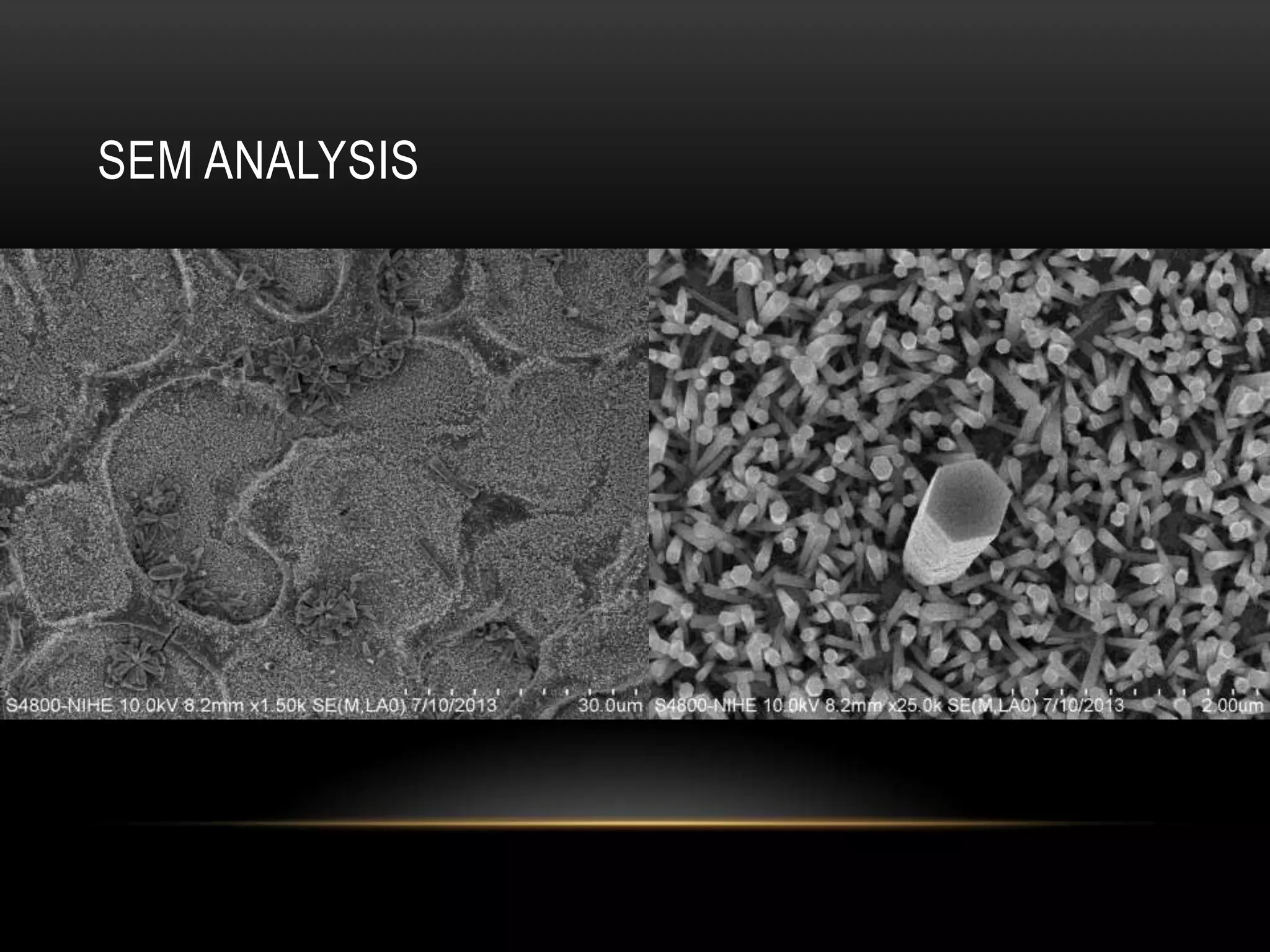
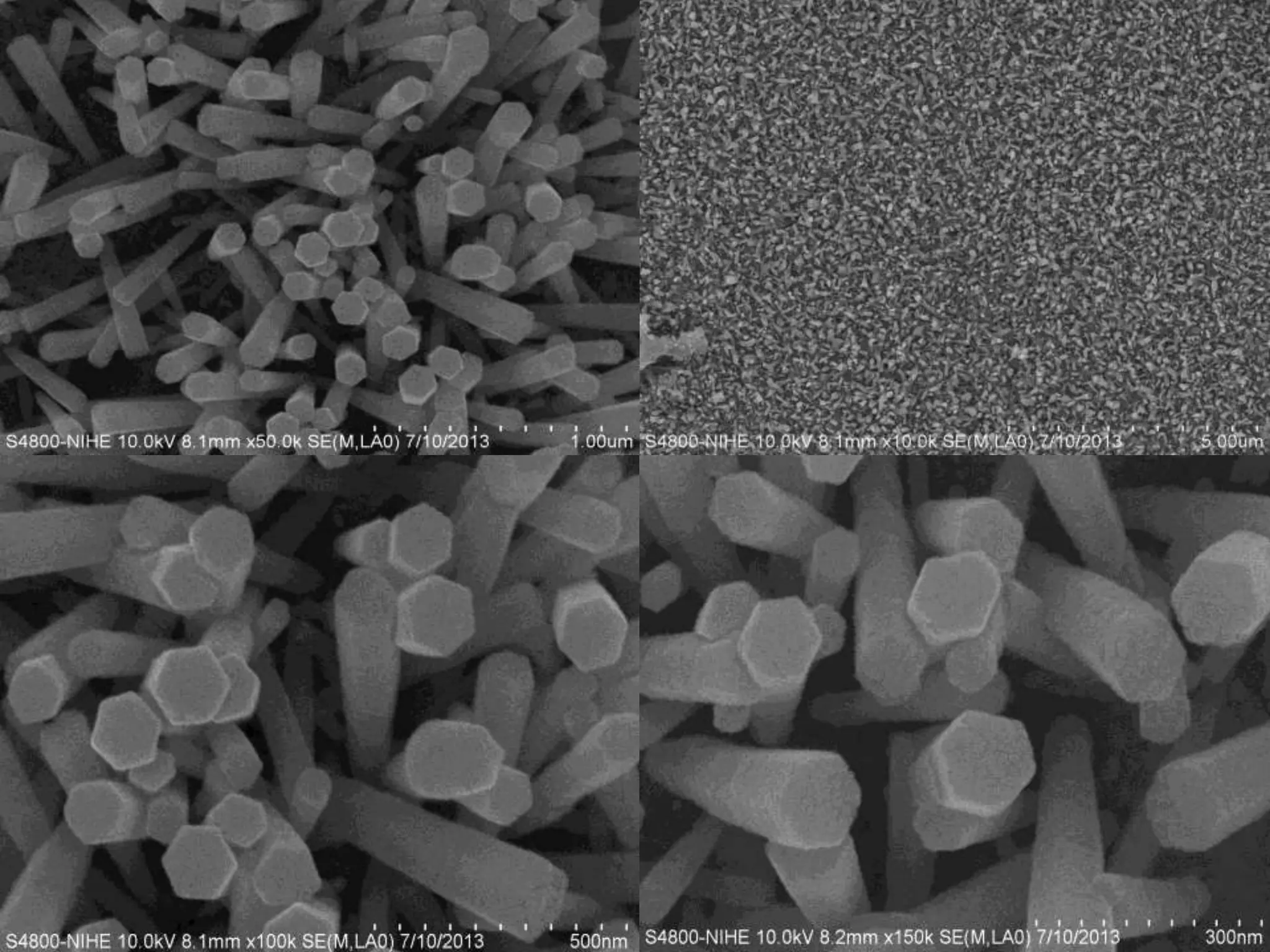
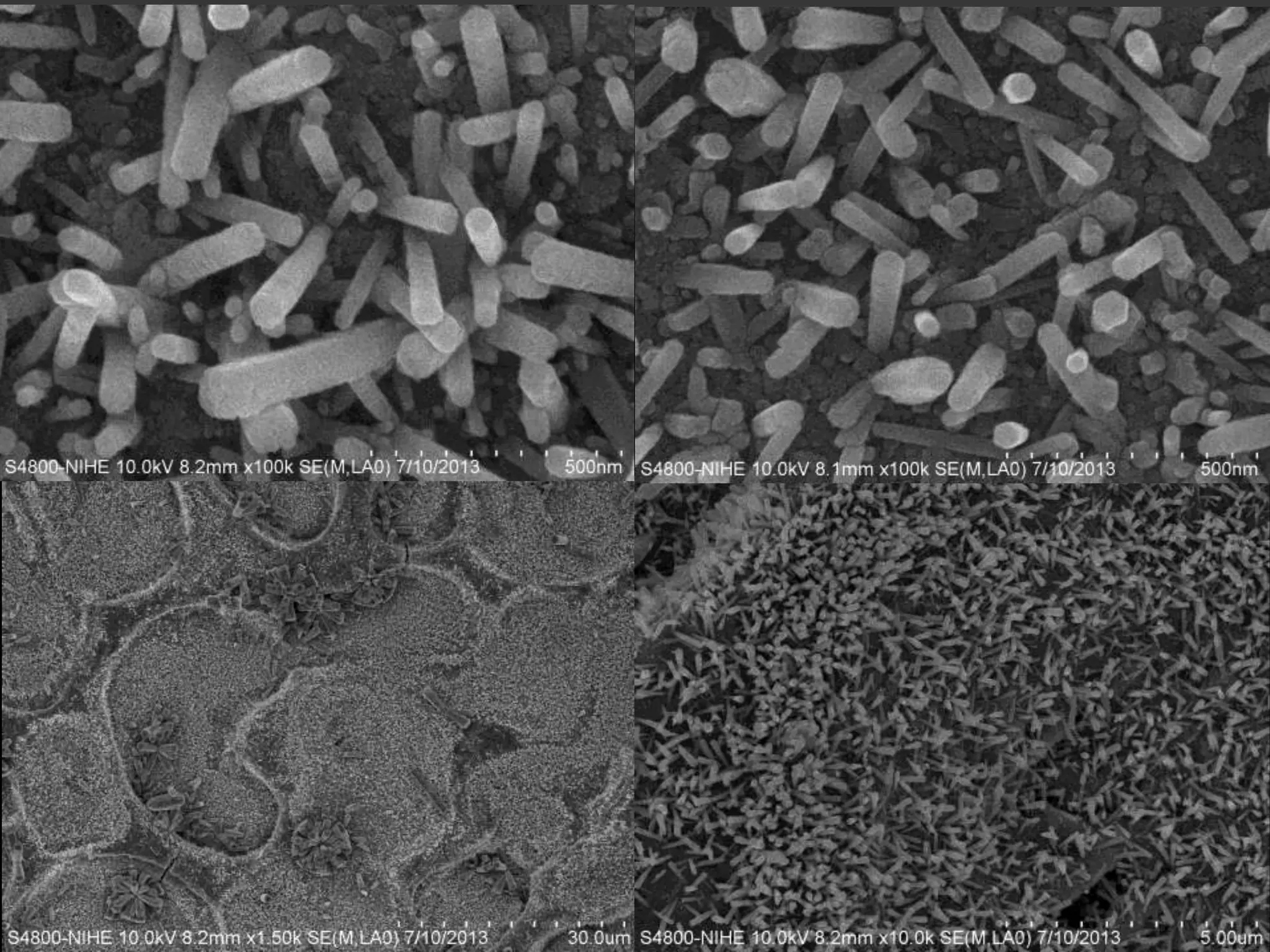
- Titanium dioxide shells were deposited on zinc oxide nanorods using a hydrothermal method. Zinc oxide nanorods were first grown on a fluorine-doped tin oxide substrate via hydrothermal synthesis using zinc nitrate hexahydrate, hexamethylenetetramine, and deionized water at 80°C for 1-3 hours. Titanium dioxide shells were then deposited on the zinc oxide nanorods by another hydrothermal treatment using titanium isopropoxide as a titanium precursor at 150°C for 5 hours. The zinc oxide-titanium dioxide core-shell nanostructures were characterized using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, UV-visible spectroscopy, and solar cell testing to analyze their structure, morphology