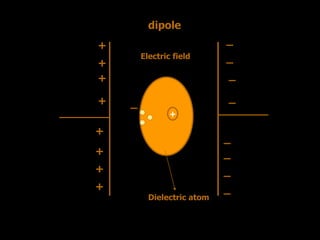
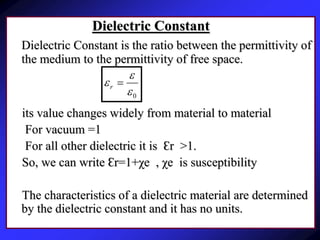
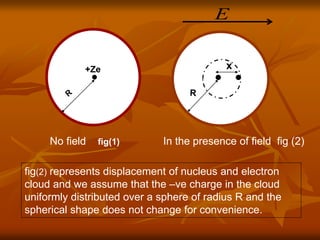
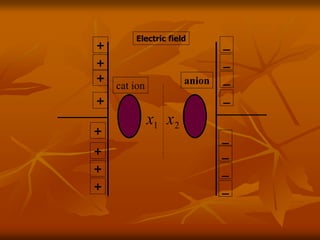
Dielectrics are materials that contain permanent or induced electric dipoles. They can be polarized by an external electric field, resulting in dipole orientation or charge displacement within the material. There are several types of polarization that can occur in dielectrics, including electronic, ionic, orientation, and space charge polarization. Dielectrics have a wide variety of applications including use in capacitors, transformers, cables, and other electrical equipment due to their insulating properties.