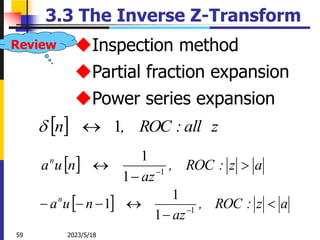
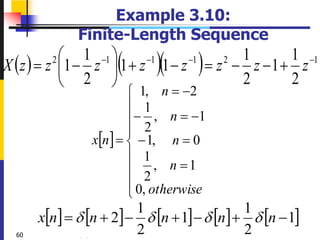
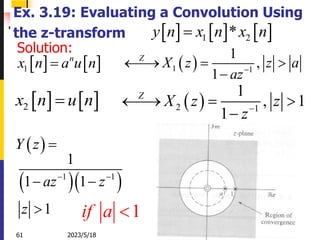
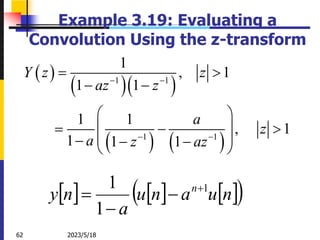
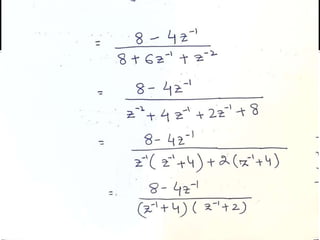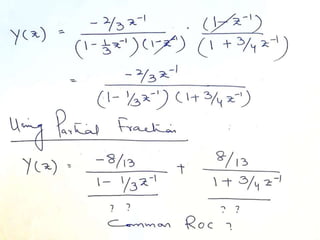The document summarizes key concepts about the z-transform, which is the discrete-time counterpart of the Laplace transform. It describes the z-transform definition and how it relates to the discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT). The region of convergence (ROC) is defined as the set of z-values where the z-transform converges. The ROC depends on whether the signal is right-sided, left-sided, or two-sided. Examples are provided to illustrate the ROC for different types of signals. Properties of the ROC like its shape and relationship to system stability and causality are also covered.


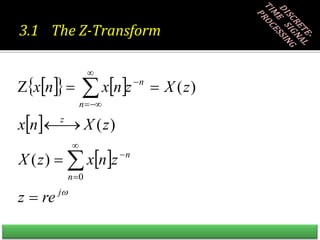
![Z-Transform
n
n
z
n
x
z
X Bilateral Z-Transform
0
n
n
X z x n z
Unilateral Z-Transform
Clearly, Bilateral and Unilateral Z-Transform are same when x[n] = 0,
for n<0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adsp17nov-230518094957-e649353b/85/ADSP-17-Nov-ppt-4-320.jpg)



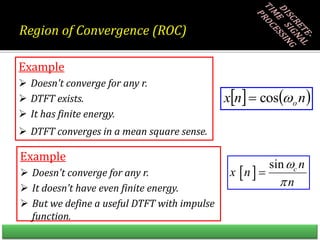
![Convergence of the z-Transform
• DTFT does not always converge
Example: x[n] = an u[n] for |a|>1 does not have a DTFT
• Complex variable z can be written as r ej so the z-
transform
convert to the DTFT of x[n] multiplied with exponential
sequence r –n
• For certain choices of r the sum
maybe made finite
Chapter 3: The Z-Transform 8
n
n
j
n
n
n
j
j
e
n
x
e
n
x
re
X
r
r
n
j
n
j
e
n
x
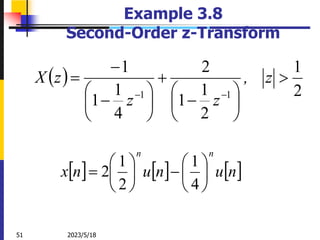
e
X
n
n
x r n
-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adsp17nov-230518094957-e649353b/85/ADSP-17-Nov-ppt-9-320.jpg)








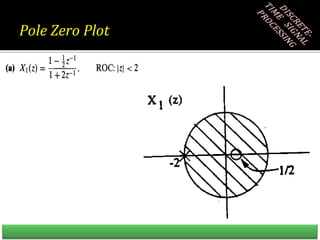
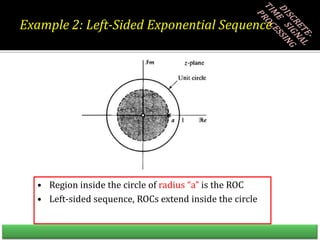
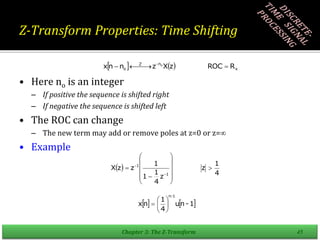
![Right-Sided Exponential Sequence
If x[n] is a Right Sided Sequence, then ROC will always extend outside the
outermost pole i.e. highest magnitude pole.
In previous example, it has been proven, since the common ROC is Z > 16
Q: Is the system mentioned in Example, a stable system?
A: For a system to be stable, it must include the unit circle. The mentioned
ROC of Z > 16 does not include the unit circle, therefore the system is
unstable.
Q: Is the system mentioned in Example, a causal system?
A: For a system to be causal, ROC must extend outside the outermost pole.
The mentioned ROC of Z > 16 shows exactly that, therefore the system is a
causal system](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adsp17nov-230518094957-e649353b/85/ADSP-17-Nov-ppt-19-320.jpg)





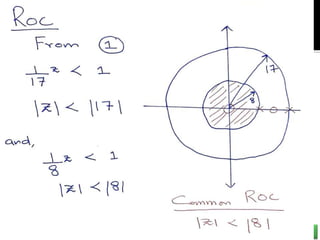
![Left-Sided Exponential Sequence
If x[n] is a Left Sided Sequence, then ROC will always be inside the innermost
pole i.e. lowest magnitude pole.
In previous example, it has been proven, since the common ROC is Z < 8
Q: Is the system mentioned in Example, a stable system?
A: For a system to be stable, it must include the unit circle. The mentioned
ROC of Z < 8 does include the unit circle, therefore the system is stable.
Q: Is the system mentioned in Example, a causal system?
A: For a system to be causal, ROC must extend outside the outermost pole.
The mentioned ROC of Z < 8 does not show that, therefore the system is non-
causal/ Anti-Causal.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adsp17nov-230518094957-e649353b/85/ADSP-17-Nov-ppt-27-320.jpg)









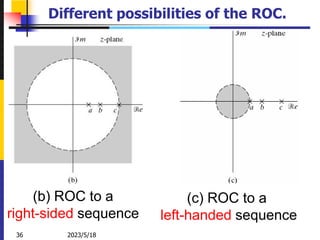
![2023/5/18
38 Zhongguo Liu_Biomedical Engineering_Shandong Univ.
Ex. 3.7 Stability, Causality, and the ROC
Consider a LTI system with impulse
response h[n]. The z-transform of h[n] i.e.
the system function H (z) has the pole-zero
plot shown in Figure. Determine the ROC,
if the system is:
(1) stable system:
(ROC include unit-circle)
(2) causal system:
(right sided sequence)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adsp17nov-230518094957-e649353b/85/ADSP-17-Nov-ppt-39-320.jpg)











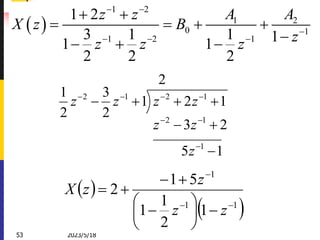
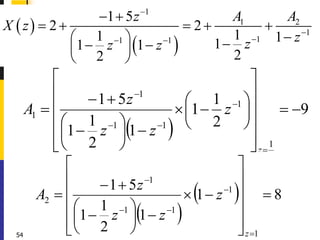

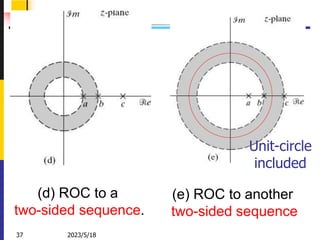
![2023/5/18
56
LTI system Stability, Causality, and ROC
For a LTI system with impulse response h[n],
if it is causal, what do we know about h[n]?
Is h[n] one-sided or two-sided sequence?
Left-sided or right-sided?
n
h
n
x
n
y
Then what do we know about the ROC of the
system function H (z)?
If the poles of H (z) are all in the unit circle,
is the system stable?
Review](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adsp17nov-230518094957-e649353b/85/ADSP-17-Nov-ppt-57-320.jpg)
![2023/5/18 Zhongguo Liu_Biomedical Engineering_Shandong Univ.
LTI system Stability, Causality, and ROC
For H (z) with the poles as shown in figure ,
1 1 1
1
1 1 1
H z
az bz cz
Unit-circle
included
can we uniquely determine h[n] ?
is the system stable ?
If ROC of H(z) is as shown
in figure, can we uniquely
determine h[n] ?
Review](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adsp17nov-230518094957-e649353b/85/ADSP-17-Nov-ppt-58-320.jpg)
![2023/5/18 Zhongguo Liu_Biomedical Engineering_Shandong Univ.
LTI system Stability, Causality, and ROC
For H (z) with the poles as shown in figure ,
1 1 1
1
1 1 1
H z
az bz cz
If the system is causal
(h[n]=0,for n<0,right-sided ),
What’s the ROC like?
If ROC is as shown in
figure, is h[n] one-sided or
two-sided? Is the system
causal or stable?
Review](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adsp17nov-230518094957-e649353b/85/ADSP-17-Nov-ppt-59-320.jpg)