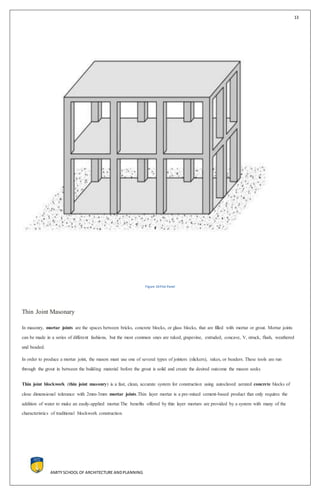
This document discusses modern construction technologies including concrete walls and floors, precast cladding panels, precast flat panel systems, volumetric modules, twin wall technology, flat slabs, thin joint masonry, concrete formwork, and precast foundations. It provides details on the materials, benefits, and processes for each technology. Case studies are presented on concrete walls and floors that discuss their affordability, ease of maintenance, and other benefits. The conclusion states that modern construction technologies can provide higher quality, more sustainable homes built faster and with less waste than conventional methods.