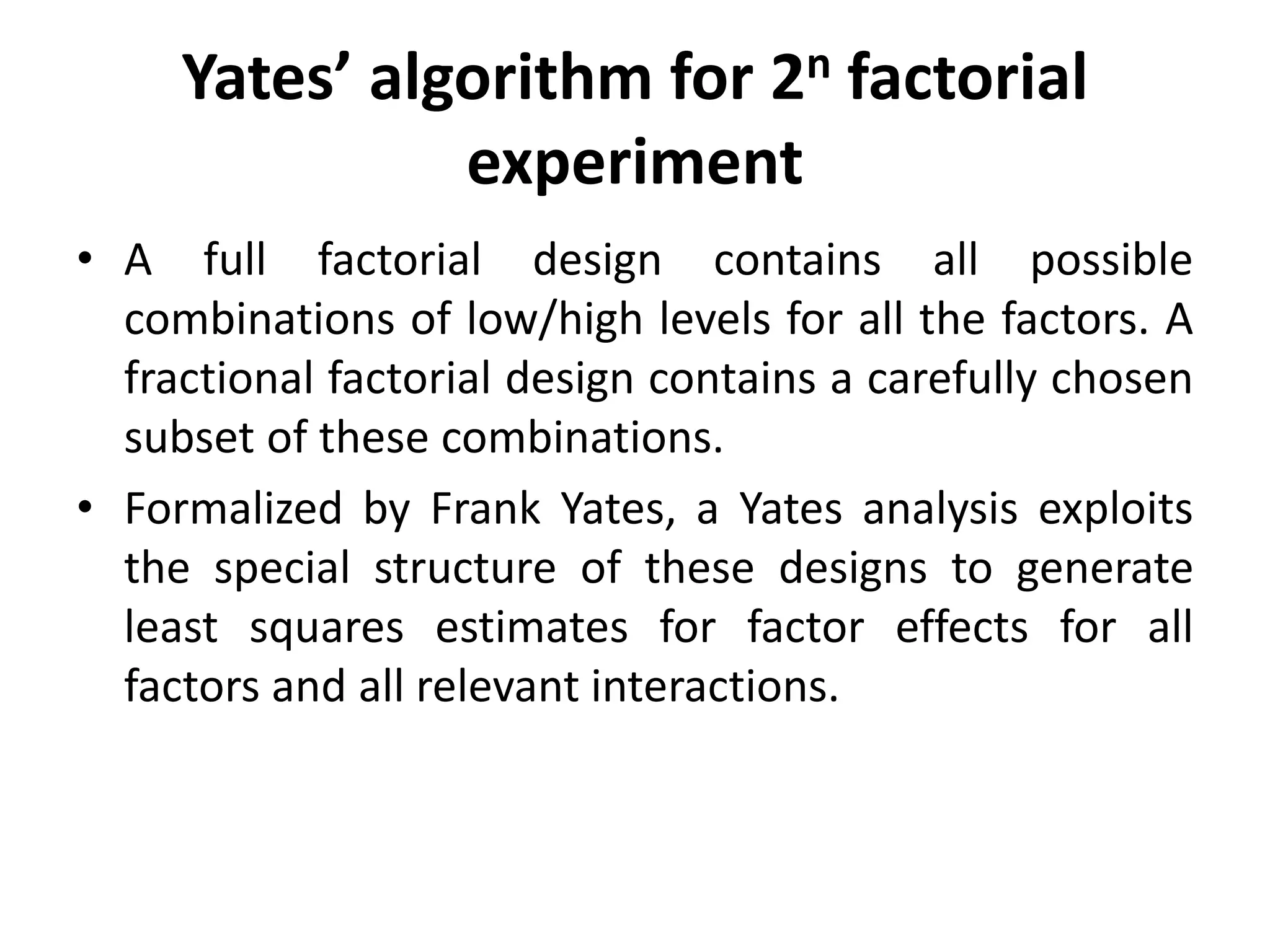
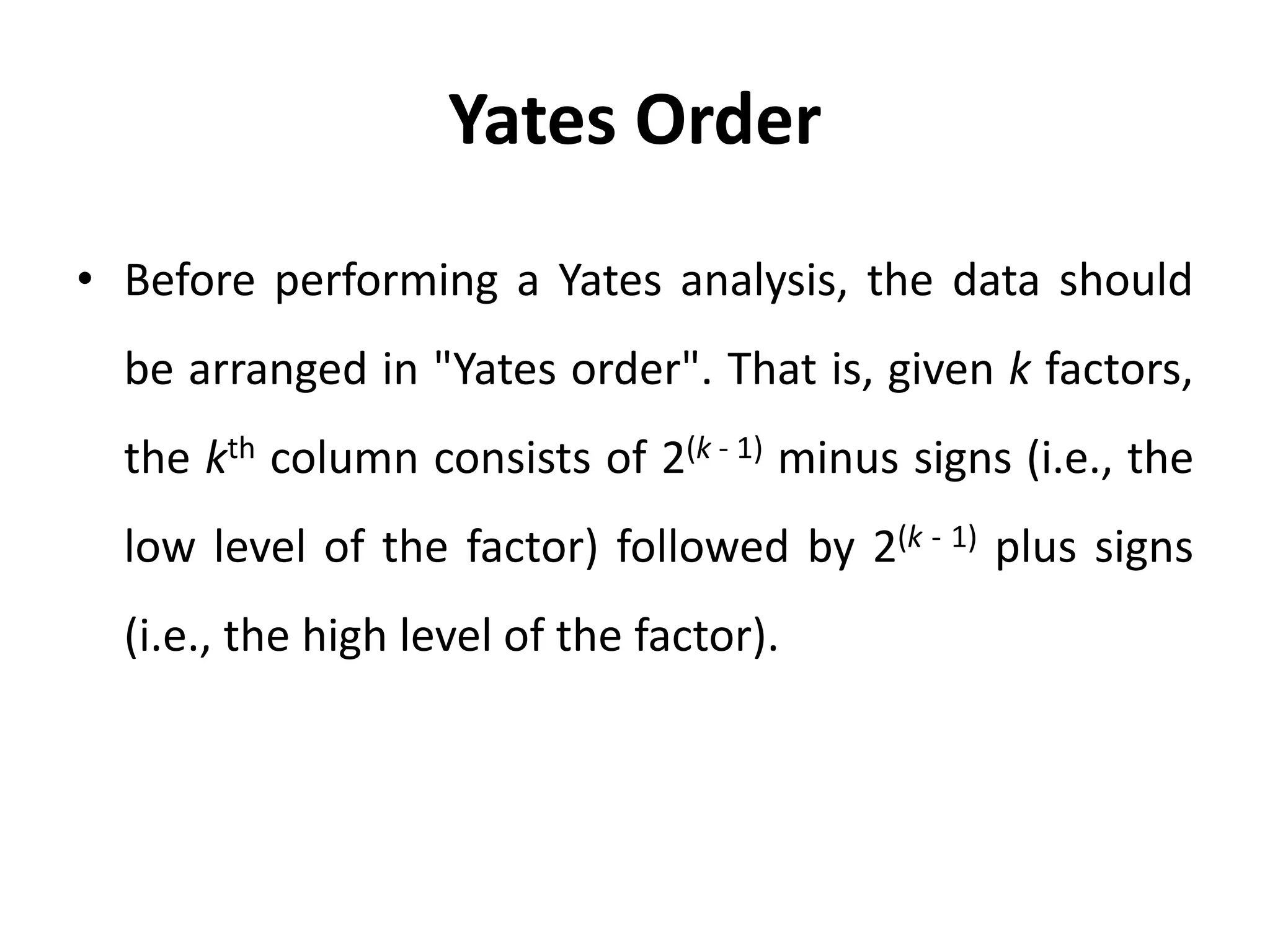
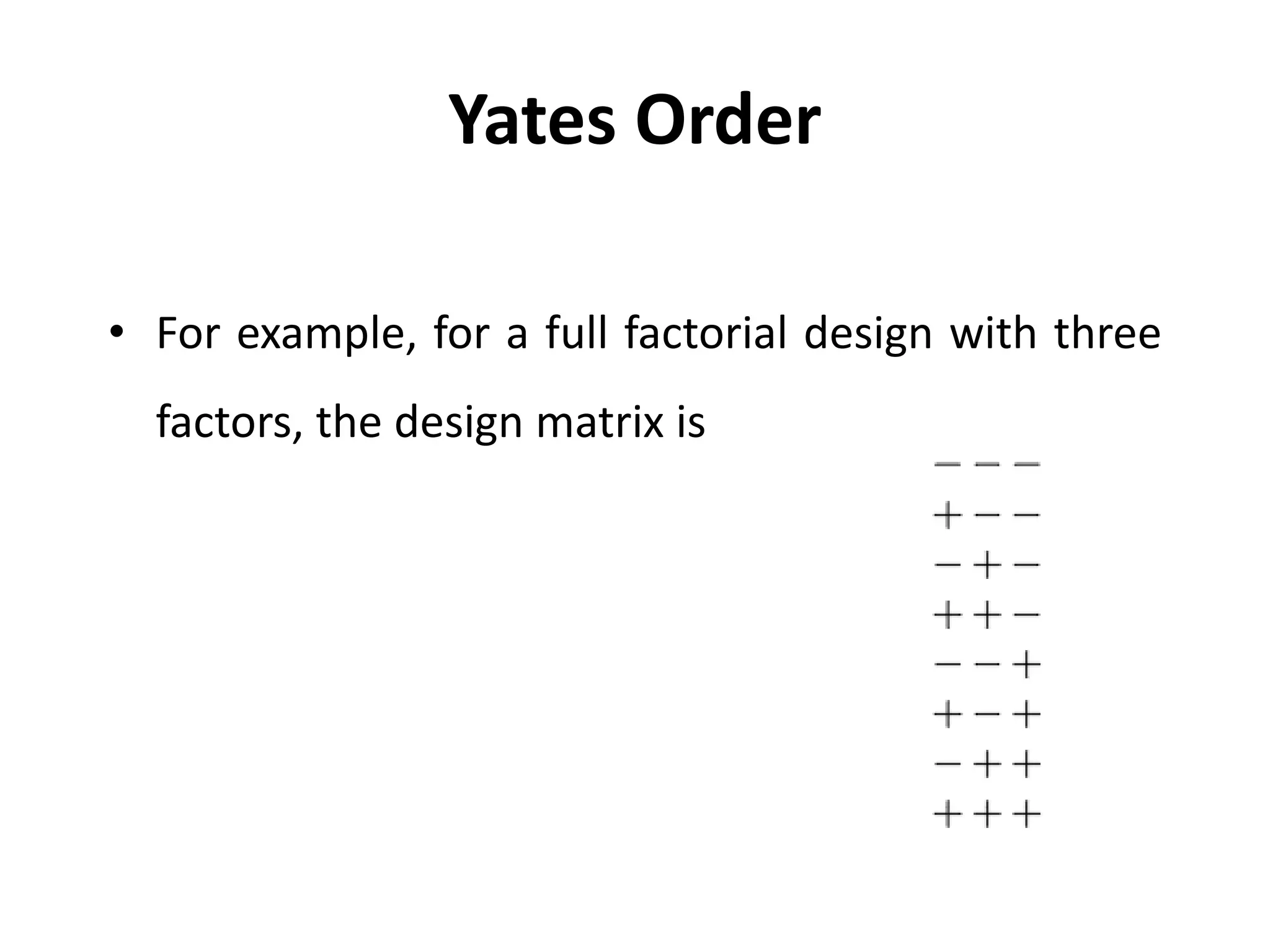
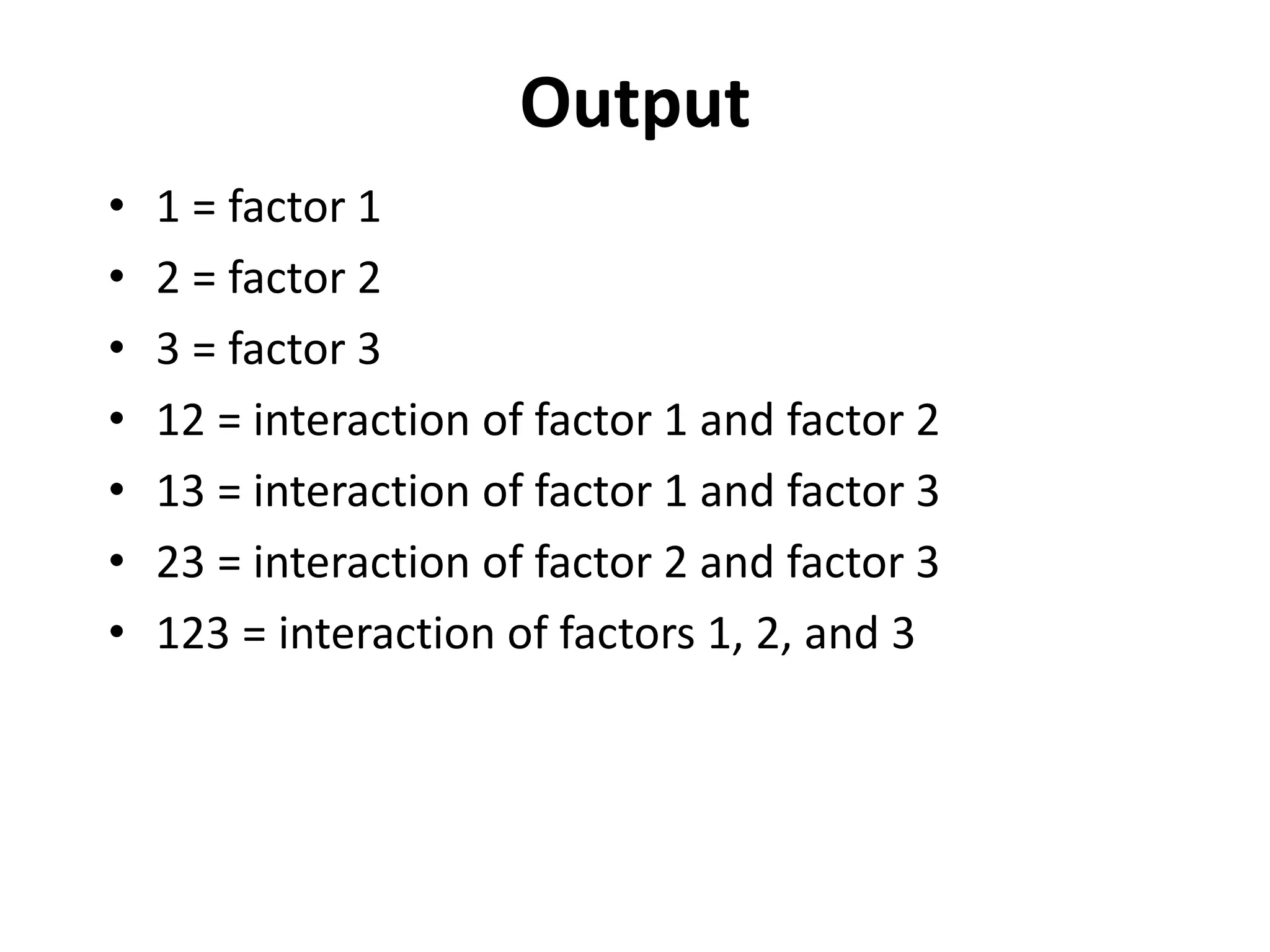
The document discusses Yates’ algorithm for 2n factorial experiments, a statistical method for analyzing data from designed experiments utilizing factorial designs. Named after statistician Frank Yates, the algorithm aims to generate least squares estimates for factor effects and interactions, providing insights such as ranked lists of factors and goodness-of-fit metrics. The document emphasizes the importance of arranging data in Yates order prior to analysis and explains the outputs generated from the analysis.