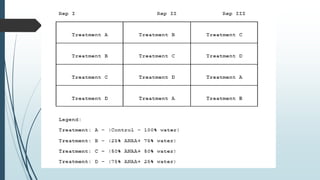
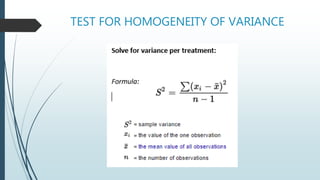
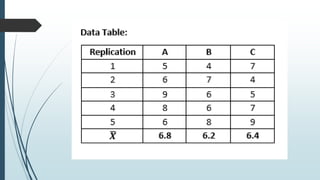
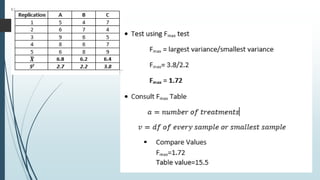
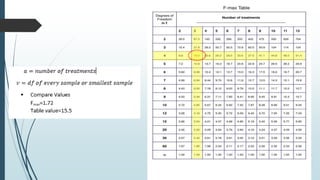
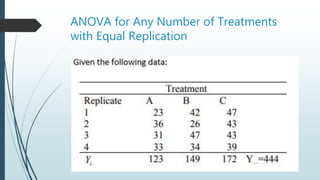
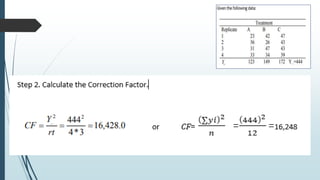
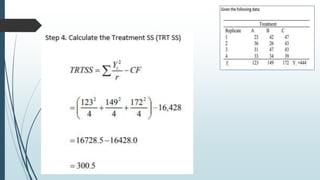
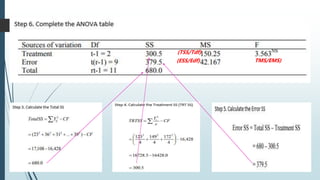
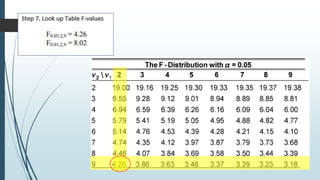
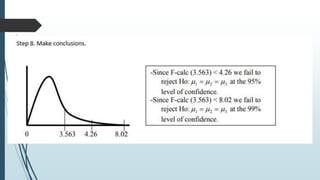
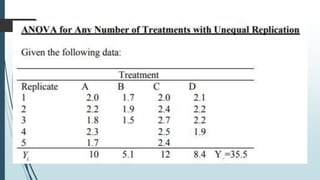
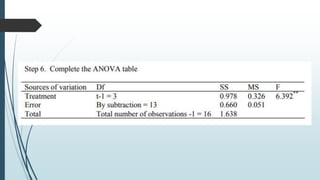
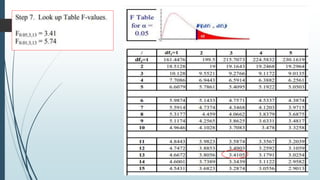
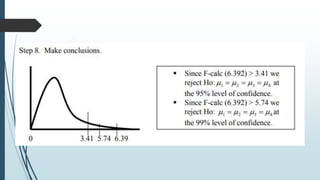
A completely randomized design (CRD) randomly assigns experimental units to different treatment groups so each unit has an equal chance of receiving any treatment. Any variation between units receiving the same treatment is considered experimental error. CRDs are best for homogeneous experimental units where environmental effects can be controlled, like laboratories. They are rarely used for field experiments with more variation. Treatments are administered at different levels or amounts. The randomization process, advantages like simplicity, and sources of variation are outlined. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) can be used to test for significant differences between treatment groups.