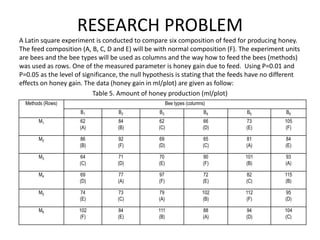
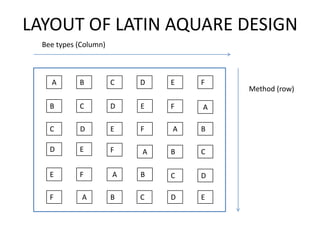
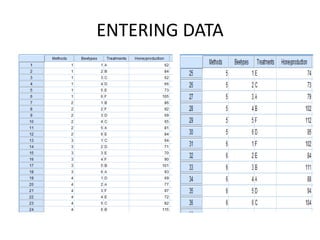
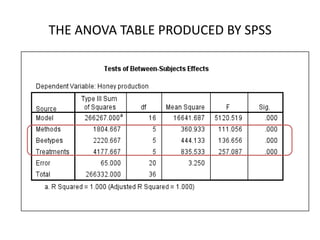
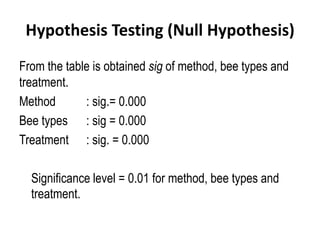
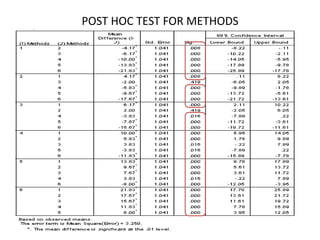
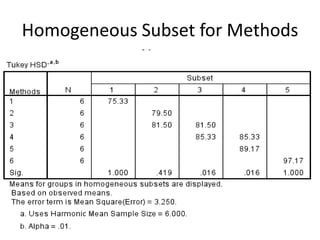
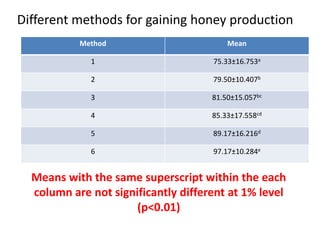
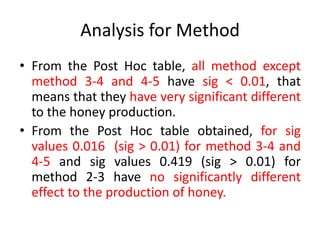
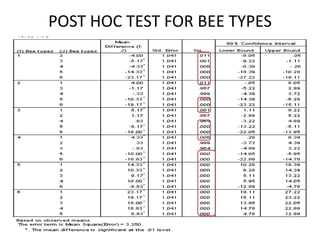
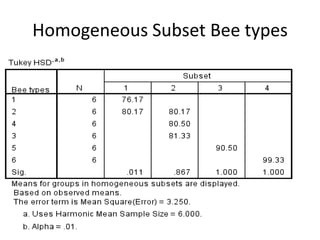
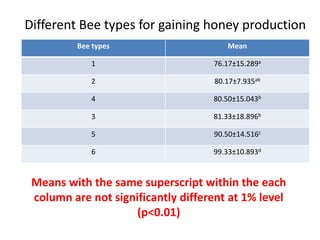
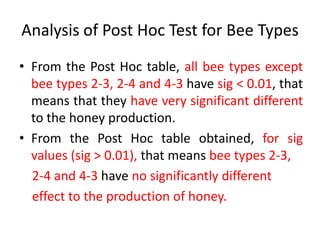
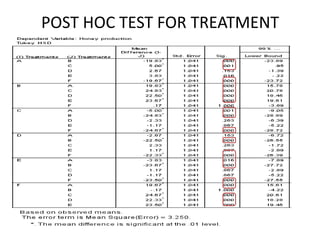
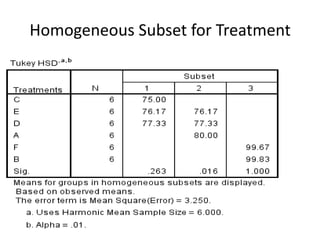
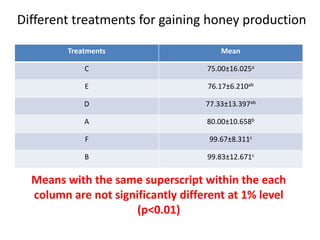
The document describes a Latin square experiment conducted to compare six feed compositions (A, B, C, D, E, F) for honey production. Bees were fed the different compositions using different methods as rows, and bee types were used as columns. The experiment measured honey gain. ANOVA and post hoc tests found the method, bee type, and feed composition all significantly affected honey gain. Method 6, bee type 6, and composition B produced the most honey and are recommended for farmers.