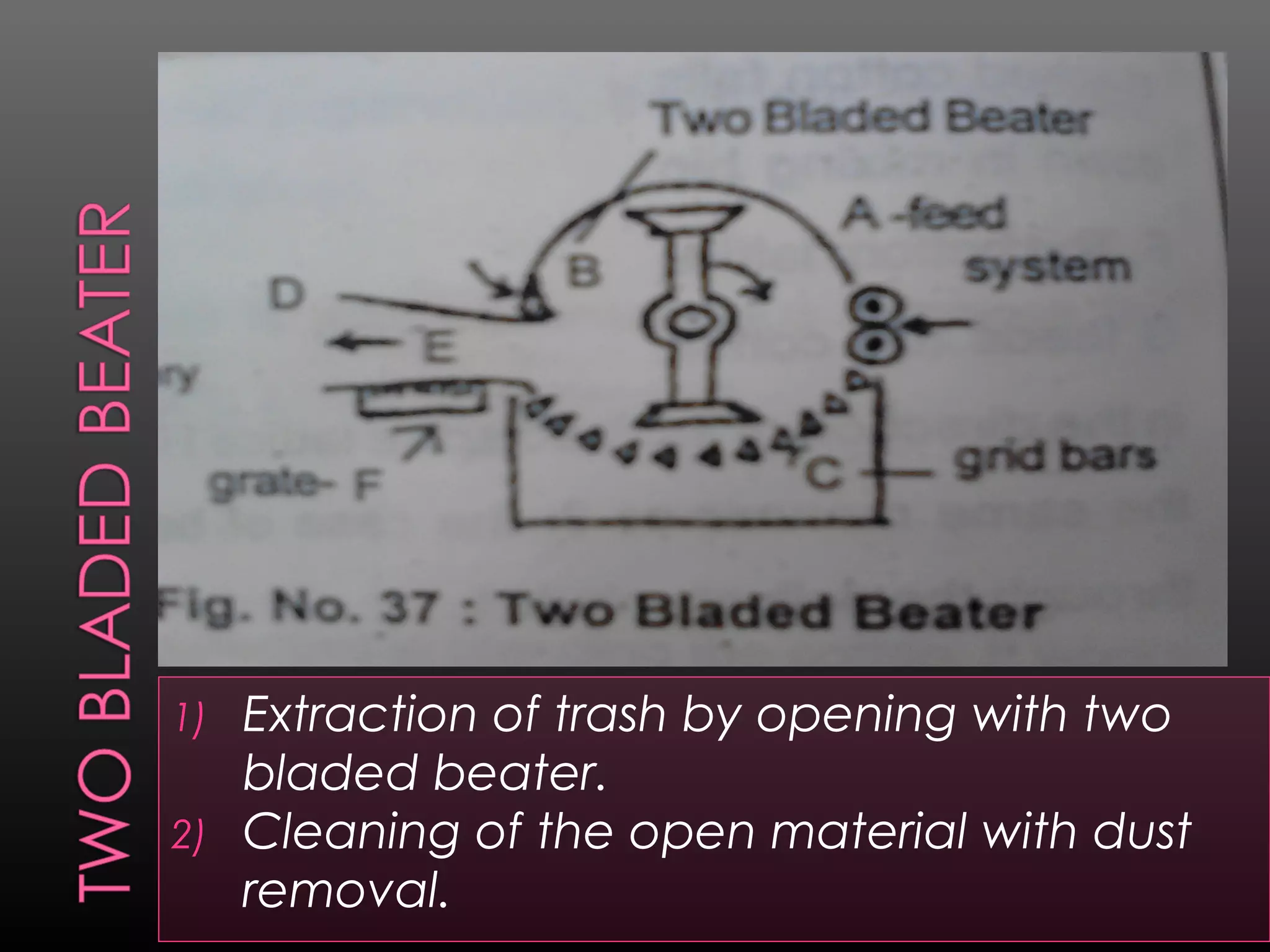
This document provides an overview of the yarn manufacturing process known as spinning. It discusses the key steps: (1) selecting textile fibers like cotton, wool, or synthetic fibers, (2) processing the fibers through blow room, carding, drawing, and ring frames to parallelize and draft them, (3) twisting the drafted fibers together to form yarn. The goal is to remove impurities from the fibers and align them in preparation for weaving or knitting into fabric.