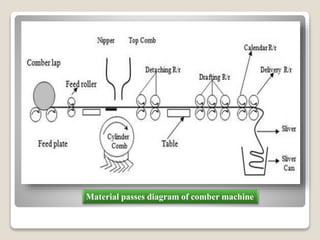
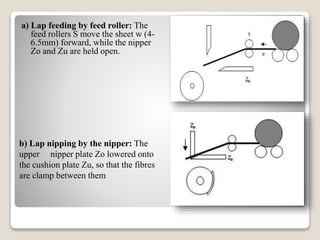
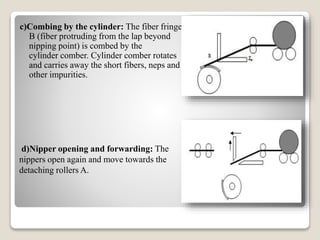
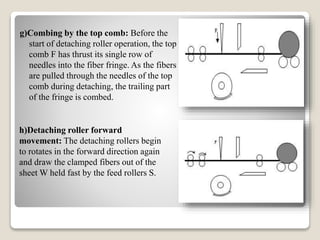
This document discusses the comber machine and the combing process. It begins with background information on the student submitting the document and the course details. It then provides 3 key points on the purpose of combing fibers. It proceeds to describe the major components of the comber machine and outlines the 10 step combing cycle. It concludes by noting that combing is used to separate out short fibers and upgrade medium staple fibers, producing higher quality combed yarn and fabric.