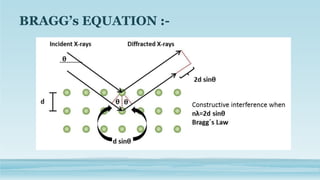
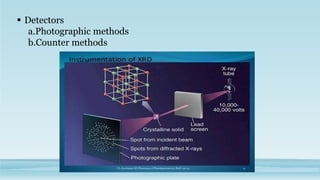
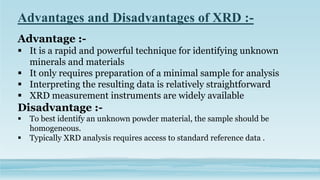
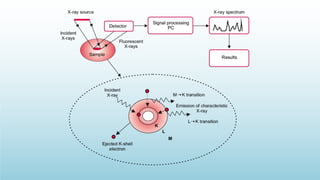
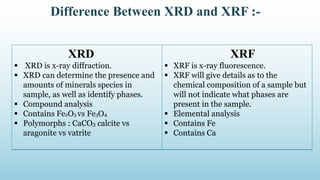
XRD and XRF are analytical techniques used to characterize materials. XRD determines the crystalline structure of materials by measuring diffraction patterns of X-rays. It can identify phases and minerals present in a sample. XRF determines the elemental composition of materials by detecting X-ray fluorescence emitted from a sample. Both techniques are non-destructive and provide qualitative and quantitative analysis of materials' composition and structure.
![XRD And XRF
PRESENTED BY :-
DR. REKHA RAM
P.G. 1ST YEAR
Guided BY :-
DR. AVADHESH KUMAR BHATT
PROFESSOR & HOD
M.D. [Ayu.]
POST GRADUATE DEPARTMENT OF
RAS SHASTRA AND BHAISHAJYA KALPANA
M.M.M. GOVERNMENT AYURVED COLLEGE,
UDAIPUR (RAJ.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xrdandxrf2-230520050247-e367df38/85/XRD-And-XRF2-pptx-1-320.jpg)