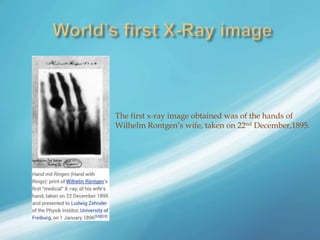
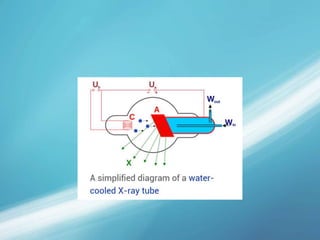
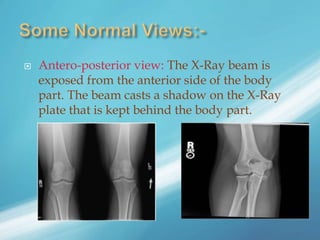
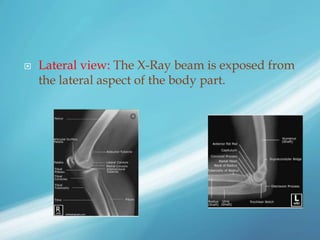
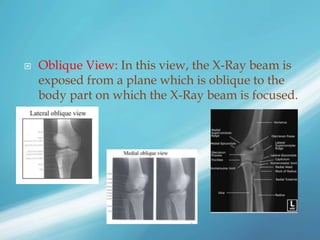
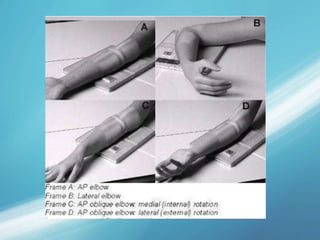
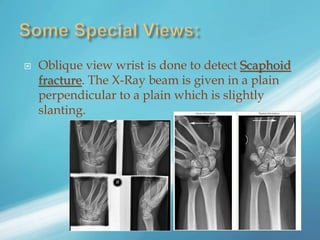
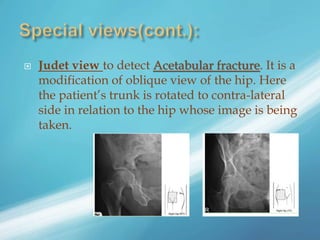
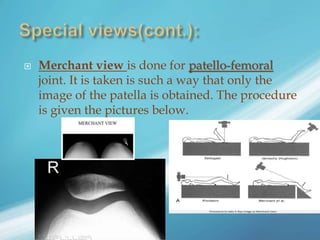
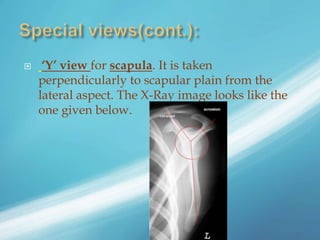
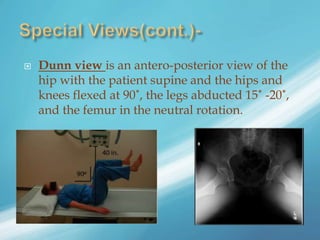
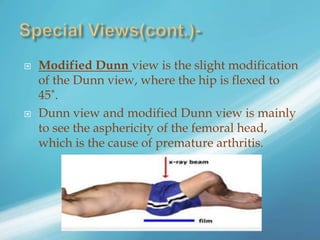
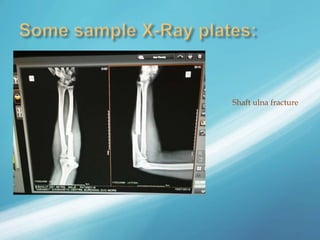
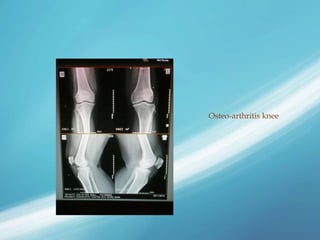
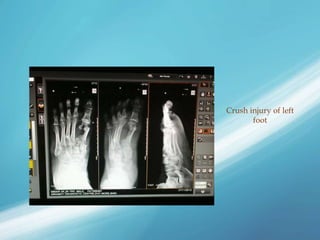
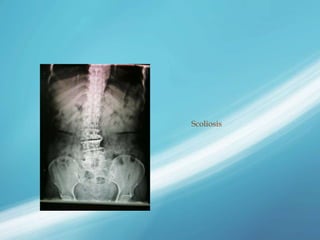
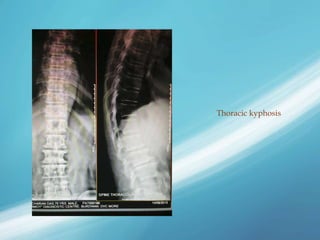
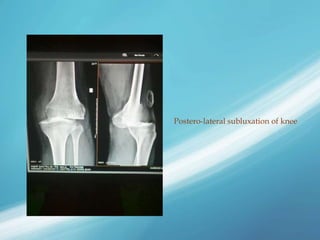
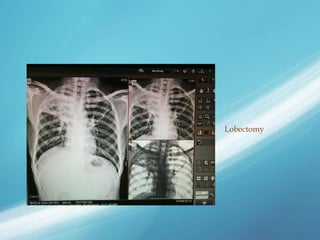
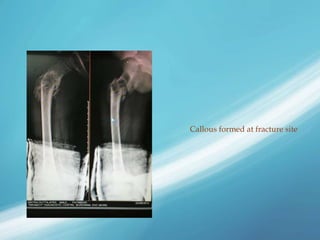
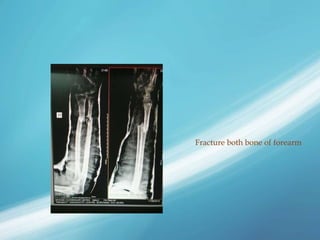
X-rays, also known as X-radiations, are a form of ionizing electromagnetic radiation discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Röntgen. They have wavelengths between 0.01 to 10 nanometers. X-rays are used widely in medical diagnostics to image bone fractures and other injuries or medical conditions. However, they also carry risks of causing cell damage and cancer due to their ionizing properties. Proper techniques and limited exposure are important to minimize these risks.