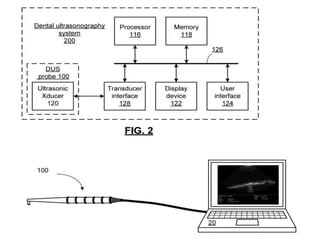
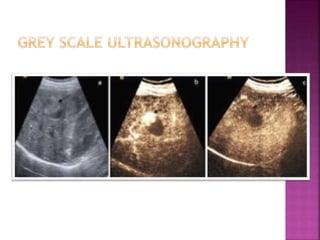
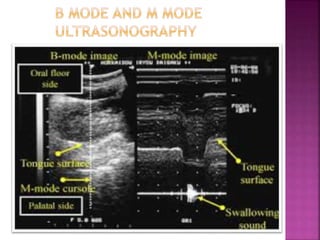
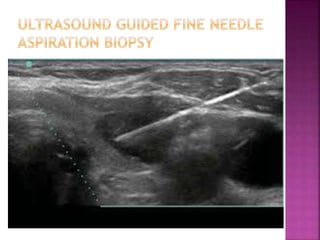
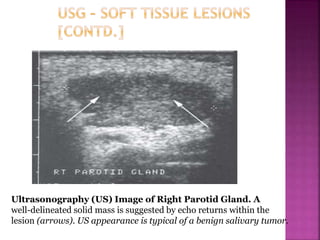
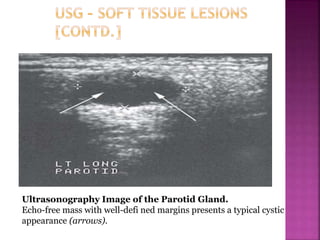
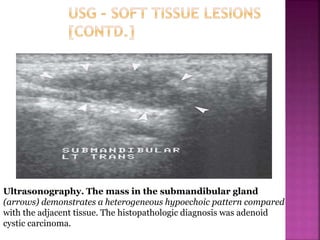
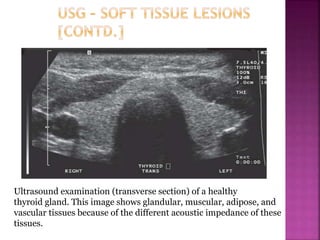
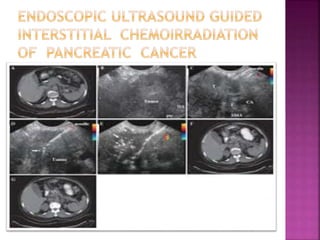
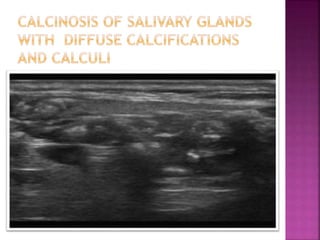
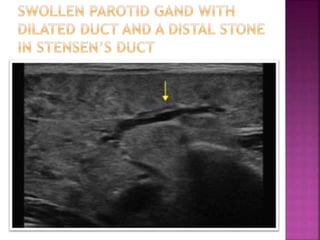
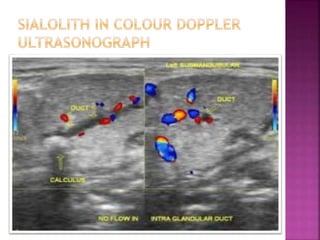
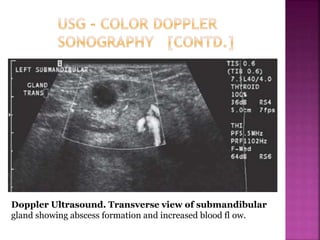
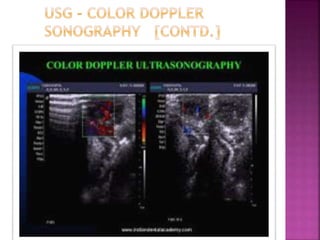
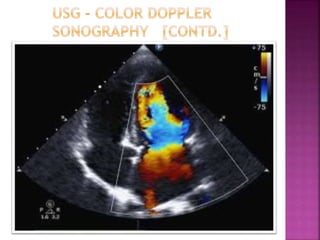
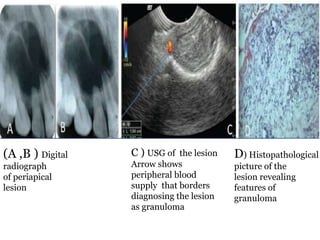
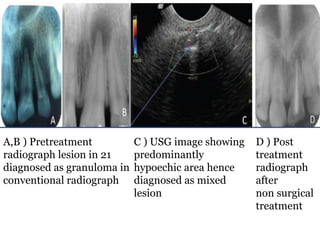
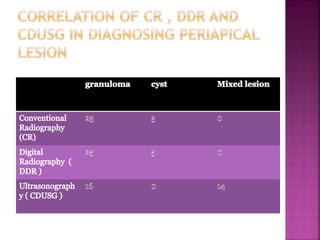
Ultrasonography uses high frequency sound waves to visualize structures inside the body. It has several applications in dentistry and oral/maxillofacial imaging. USG can detect fractures, lesions, salivary stones, and blood flow. The piezoelectric transducer converts electrical pulses into ultrasonic waves, which reflect off tissues. Differences in tissue impedance allow visualization of structures. Doppler ultrasonography assesses blood flow direction/velocity. USG provides a low-cost, non-invasive way to diagnose and monitor conditions of the oral cavity, jaws, and salivary glands.