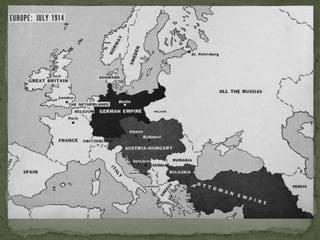
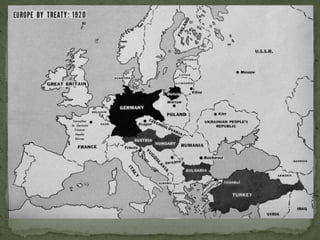
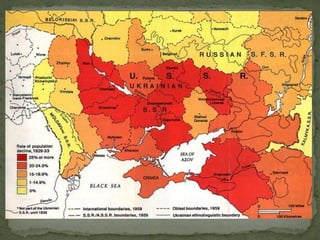
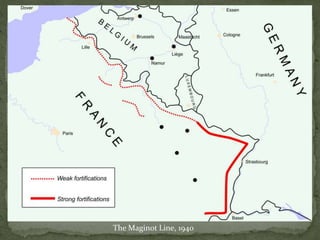
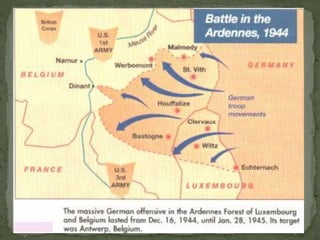
The document provides a detailed overview of the political and military events leading up to and during World War II. It describes the rise of dictators like Hitler, Mussolini, and Hirohito in Europe and Asia in the 1930s. As nationalist and militarist governments took power, they increasingly violated international treaties and invaded neighboring countries. While Western democracies attempted appeasement, war broke out in 1939 with Germany's invasion of Poland. The document then outlines the major military campaigns and turning points of the war in Europe and the Pacific theater between 1939-1945.