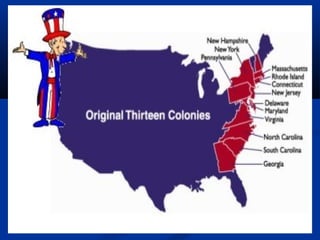
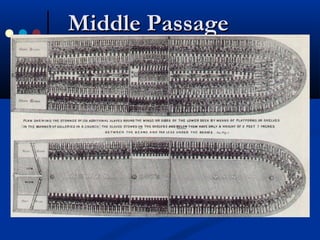
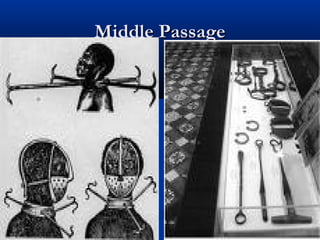
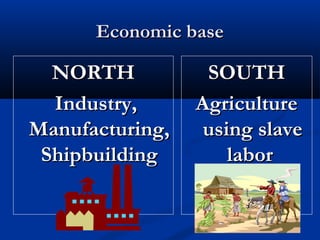
The geographic diversity of colonial North America influenced its economic, social, and political development in several ways:
- The New England colonies had poor rocky soil but abundant forests, leading to economies focused on lumber, fishing, shipbuilding, and trade. Town meetings encouraged direct democracy. Religion, particularly Puritanism, was highly influential in social and educational structures.
- The Middle colonies occupied a region with long growing seasons and fertile soil, allowing cash crops like grains and the rise of large cities. Wealthy landowners had significant political and economic power.
- Plantation agriculture flourished in the Southern colonies, made possible through the use of slave labor to produce lucrative crops like tobacco and rice. The hot climate