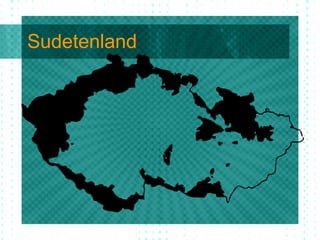
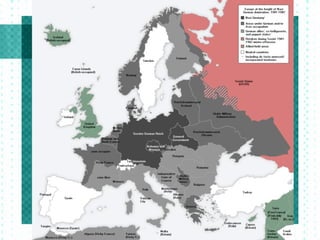
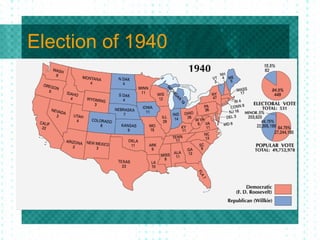
The document summarizes the rise of fascism in Europe in the 1930s and the path to war. It describes how Germany, Italy, and Japan invaded neighboring countries and withdrew from the League of Nations. Britain and France pursued a policy of appeasement by allowing Germany to annex parts of Czechoslovakia. Isolationism in the US grew due to the Great Depression and events of WWI. FDR began preparing the US for potential war by increasing defense spending in 1940 despite America First Committee opposition to intervention. WWII began with the Nazi invasion of Poland in 1939.