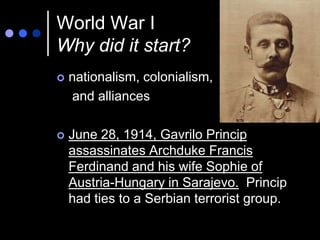
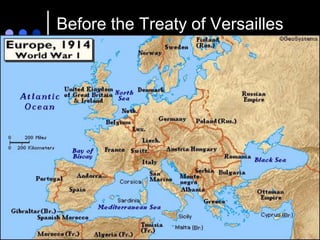
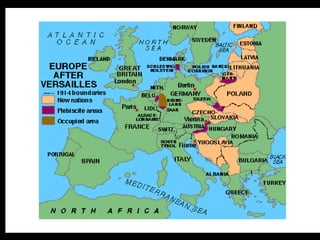
World War I, also known as the Great War, was a global war centered in Europe that began in 1914 and lasted until 1918. It started as a conflict between Austria-Hungary and Serbia but grew to include many of the great powers of Europe and beyond, divided along the lines of the Allied and Central Powers. Trench warfare and new industrial weapons led to unprecedented casualties over four years before an Allied victory.