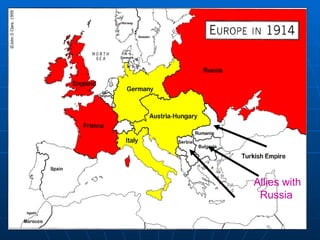
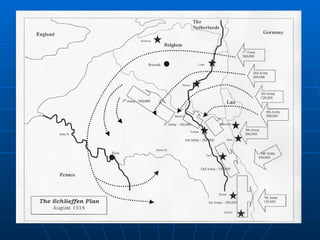
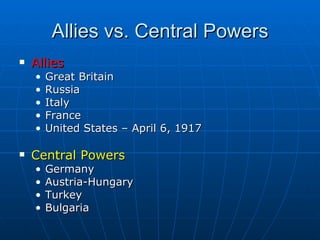
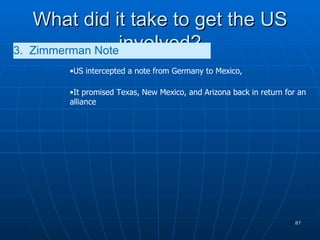
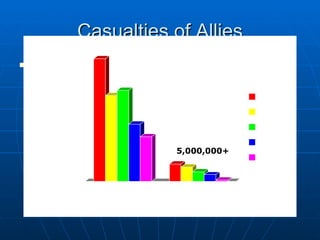
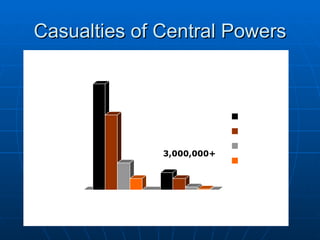
The document provides background information on the causes and early events of World War 1. It discusses the militarism, alliances, nationalism, and imperialism that contributed to rising tensions between European powers in the early 20th century. It then outlines the key events of 1914 that pulled major countries into the war, including the assassination of Archduke Ferdinand, Austria-Hungary's declaration of war on Serbia, and Germany's invasion of Belgium which led Britain to join the conflict.