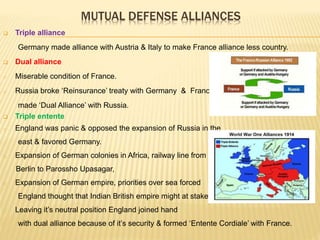
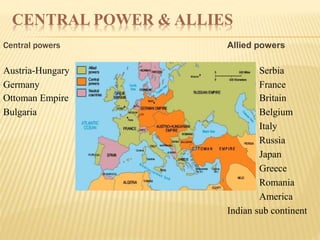
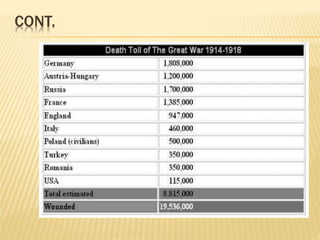
The document discusses the First World War, outlining its causes, significant battles, and the eventual consequences, including political, economic, and colonial outcomes. It highlights the involvement of various countries, the formation of alliances, and the impact of industrial advancements on warfare. The Treaty of Versailles and the establishment of the League of Nations are noted as critical outcomes of the war, aimed at preventing future conflicts.