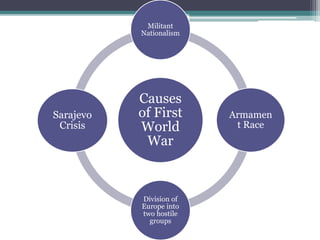
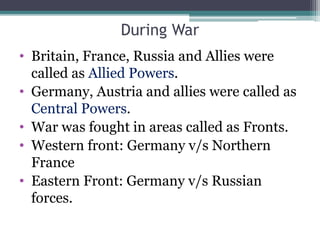
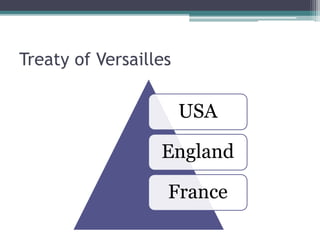
The First World War began in 1914 and ended in 1918. Some of the key causes included militant nationalism, an arms race between European powers, and the division of Europe into opposing alliances. The immediate cause was the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary by Serbian nationalists. This led Austria-Hungary to declare war on Serbia, drawing in other allied countries. After years of fighting and millions of casualties, Germany surrendered in 1918. The Treaty of Versailles established harsh peace terms for Germany and redrew borders in Europe. It also created the League of Nations to promote international cooperation and prevent future wars.