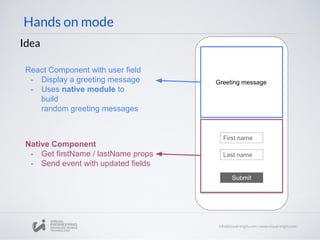
The document discusses building native components and modules for React Native applications. It provides guidance on creating native modules and components for both iOS and Android platforms. For native modules, it describes how to expose methods and properties to JavaScript. For native components, it explains how to create custom native views and expose their properties and events to React components.











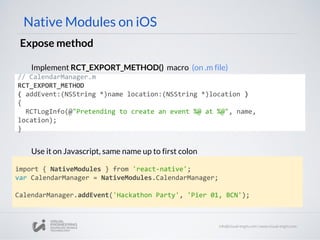


![Native Modules on iOS
Example with NSDictionary
// CalendarManager.m
RCT_EXPORT_METHOD
( addEvent:(NSString *)name details:(NSDictionary *)details ){
NSString *location = [RCTConvert NSString:details[@"location"]];
NSDate *time = [RCTConvert NSDate:details[@"time"]];
...
}
//JS
CalendarManager.addEvent('Birthday Party',
{
location: '4 Privet Drive, Surrey',
time: date.getTime(),
description: '...'
})
Getting data on iOS
Sending data from JS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/react-native-the-native-side-160817140854/85/Workshop-26-React-Native-The-Native-Side-16-320.jpg)


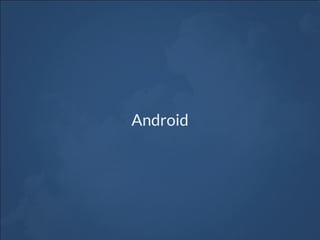



![Native Modules on Android
Callbacks
Java
public class UIManagerModule extends ReactContextBaseJavaModule {
...
@ReactMethod
public void measureLayout(
int tag,
int ancestorTag,
Callback errorCallback,
Callback successCallback) {
try {
measureLayout(tag, ancestorTag, mMeasureBuffer);
float relativeX = PixelUtil.toDIPFromPixel(mMeasureBuffer[0]);
float relativeY = PixelUtil.toDIPFromPixel(mMeasureBuffer[1]);
float width = PixelUtil.toDIPFromPixel(mMeasureBuffer[2]);
float height = PixelUtil.toDIPFromPixel(mMeasureBuffer[3]);
successCallback.invoke(relativeX, relativeY, width, height);
} catch (IllegalViewOperationException e) {
errorCallback.invoke(e.getMessage());
}
}
...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/react-native-the-native-side-160817140854/85/Workshop-26-React-Native-The-Native-Side-26-320.jpg)

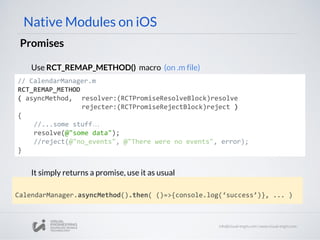
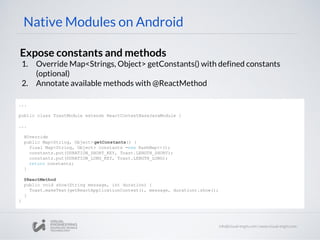
![Native Modules on Android
Promises
Java
public class UIManagerModule extends ReactContextBaseJavaModule {
...
@ReactMethod
public void measureLayout(
int tag,
int ancestorTag,
Promise promise) {
try {
measureLayout(tag, ancestorTag, mMeasureBuffer);
WritableMap map = Arguments.createMap();
map.putDouble("relativeX", PixelUtil.toDIPFromPixel(mMeasureBuffer[0]));
map.putDouble("relativeY", PixelUtil.toDIPFromPixel(mMeasureBuffer[1]));
map.putDouble("width", PixelUtil.toDIPFromPixel(mMeasureBuffer[2]));
map.putDouble("height", PixelUtil.toDIPFromPixel(mMeasureBuffer[3]));
promise.resolve(map);
} catch (IllegalViewOperationException e) {
promise.reject(e);
}
}
...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/react-native-the-native-side-160817140854/85/Workshop-26-React-Native-The-Native-Side-28-320.jpg)




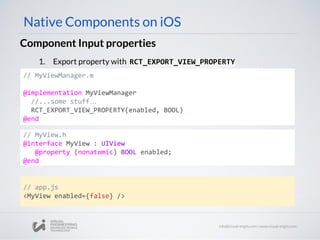
![// MyViewManager.h
#import "MyView.h"
#import "RCTViewManager.h"
@interface RCTMapManager :
RCTViewManager
@end
Basics
Native Components on iOS
- (UIView *)view
{
return [[MyView alloc] init];
}
2 . Implement method - (UIView *) view in MyViewManager.m
1. Subclass RCTViewManager and export it with RCT_EXPORT_METHOD()
Consider we already have an iOS custom view, for example, MyView
// MyViewManager.m
#import
"MyViewManager.h"
@implementation RCTMapManager
RCT_EXPORT_MODULE()
@end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/react-native-the-native-side-160817140854/85/Workshop-26-React-Native-The-Native-Side-33-320.jpg)
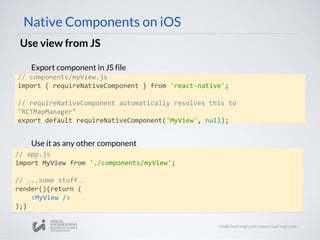
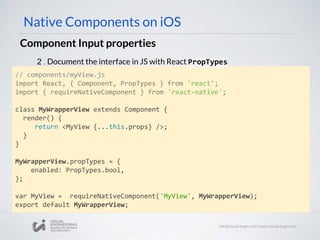

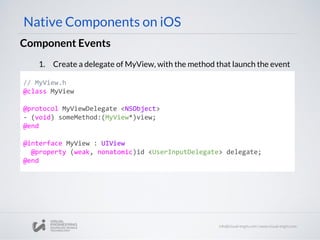
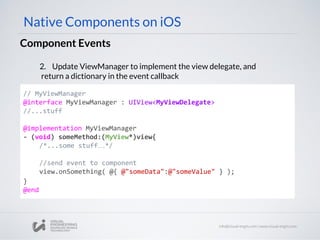
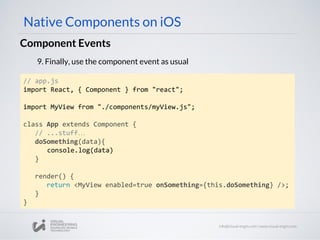
![Component Events
// MyViewManager
- (UIView *)view
{
MyView* view = [[MyView alloc] init];
view.delegate = self;
Return view;
}
Native Components on iOS
3. Update ViewManager (UIView*) view method to assign delegate
4. Export RCTBubblingEventBlock property on ViewManager
// MyViewManager
@implementation MyViewManager
//...stuff...
RCT_EXPORT_VIEW_PROPERTY(onSomething, RCTBubblingEventBlock)
@end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/react-native-the-native-side-160817140854/85/Workshop-26-React-Native-The-Native-Side-40-320.jpg)






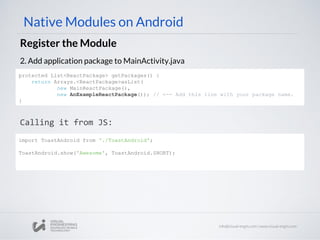
![Native Components on Android
3. Register the ViewManager
Calling it from JS
@Override
public List<ViewManager> createViewManagers(
ReactApplicationContext reactContext) {
return Arrays.<ViewManager>asList(
new ReactImageManager()
);
}
// ImageView.js
import { PropTypes } from 'react';
import { requireNativeComponent, View } from'react-native';
var iface = {
name: 'ImageView',
propTypes: {
src: PropTypes.string,
borderRadius: PropTypes.number,
resizeMode: PropTypes.oneOf(['cover', 'contain', 'stretch']),
...View.propTypes // include the default view properties
},
};
module.exports = requireNativeComponent('RCTImageView', iface);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/react-native-the-native-side-160817140854/85/Workshop-26-React-Native-The-Native-Side-49-320.jpg)