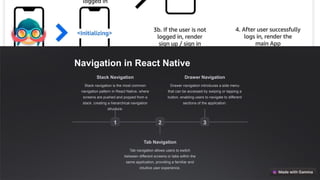
React Native is an open-source framework developed by Facebook for building high-quality mobile applications using a single codebase for both iOS and Android. It utilizes React's component-based architecture and offers core components, state management options like Redux and MobX, and various navigation patterns. The framework supports responsive designs and cross-platform deployment, enhancing user experiences and streamlining app development processes.