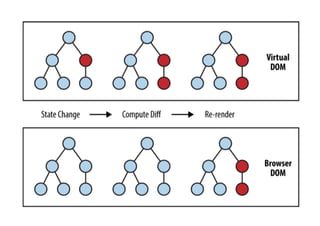
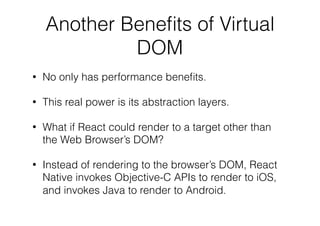
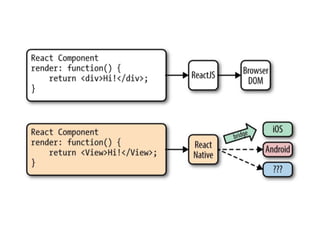
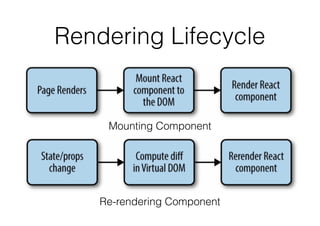
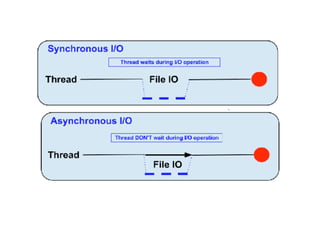
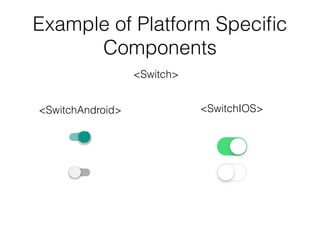
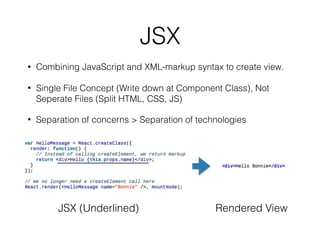
The document outlines an introductory lecture on React Native by Dr. Kobkrit Viriyayudhakorn, detailing course structure, grading, and project requirements for creating mobile applications. It provides an overview of React Native as a JavaScript framework for building iOS and Android apps, highlighting its benefits, such as cross-platform development and efficient debugging. Key concepts discussed include the use of JSX for rendering views, performance advantages of the virtual DOM, and the integration of native APIs.