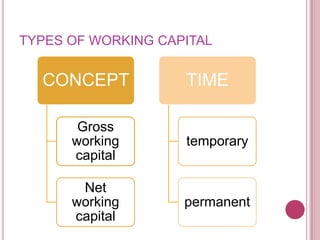
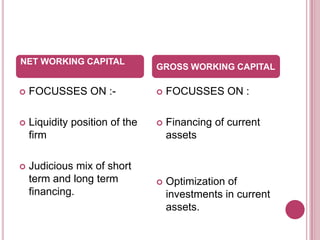
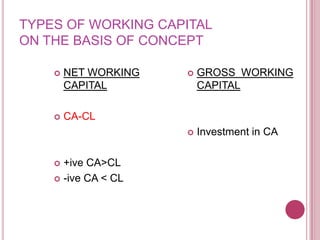
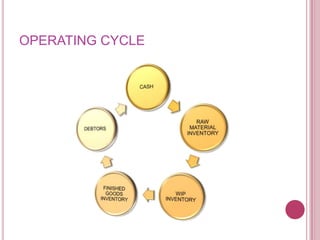
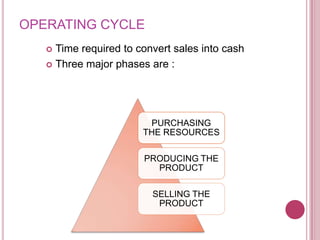
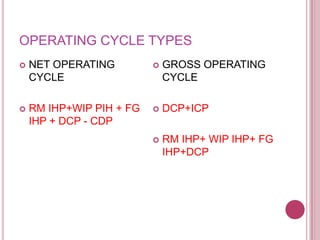
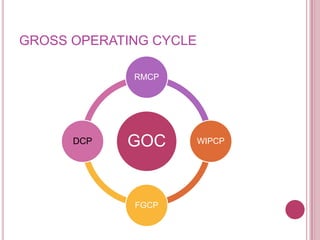
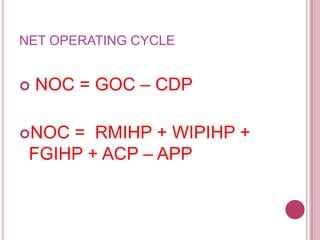
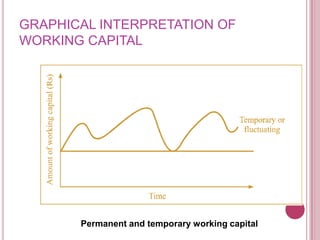
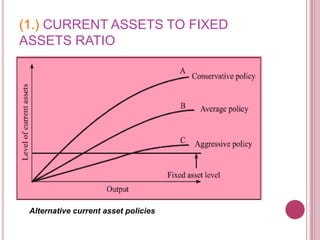
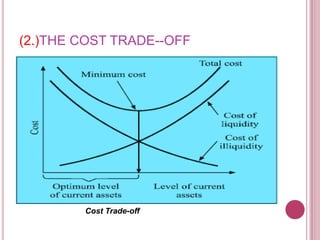
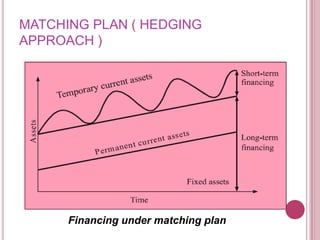
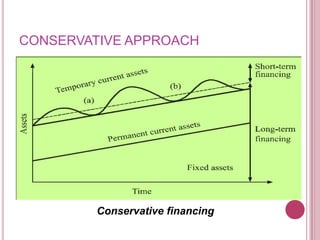
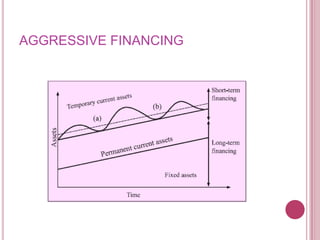
The document defines working capital as the capital required to finance short-term operating needs like current assets. It discusses the different types of working capital including gross and net working capital. It also covers key concepts related to working capital management such as operating cycle, determinants of working capital needs, and approaches to financing current assets using long-term vs short-term sources of funds.