Embed presentation
Downloaded 42 times
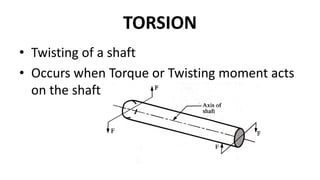
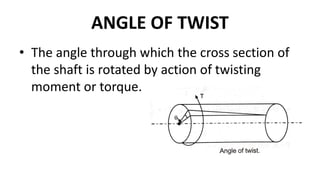
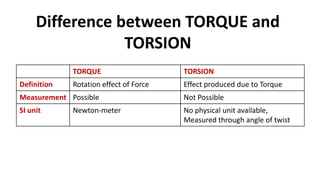
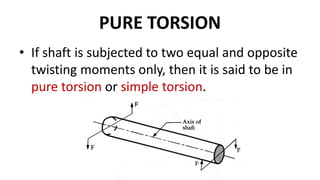


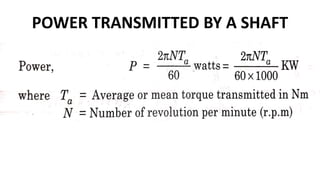


Torsion refers to the twisting of a shaft when a torque or twisting moment acts on it. The angle of twist is defined as the angle through which the shaft's cross section rotates due to the torque. Torque causes rotation, while torsion is the effect produced by torque. Torsion occurs in a shaft when it is subjected to two equal and opposite twisting moments, known as pure torsion. The torsion equation relates the angle of twist in a shaft to the applied torque based on certain assumptions about the shaft's material properties and dimensions. Power can be transmitted through a rotating shaft by applying torque that causes torsion.









