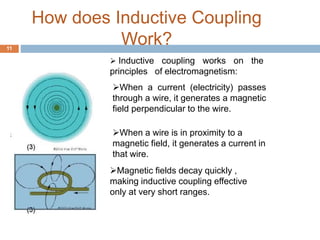
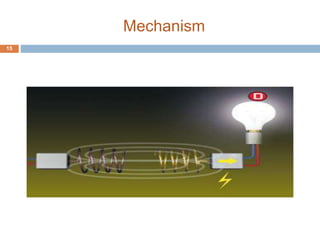
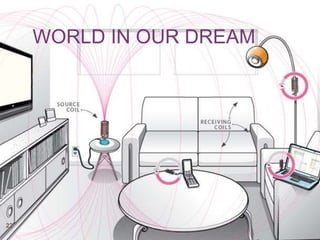
This document discusses wireless power transmission (WiTricity). It provides a brief history of wireless power beginning with Nikola Tesla's experiments in the late 1800s. In 2007, MIT researchers successfully transmitted 60 watts of power over 2 meters without wires using resonant inductive coupling. The document describes three types of wireless power transmission - short range inductive coupling, medium range resonant induction, and long range electromagnetic waves. It discusses the mechanisms, applications, advantages, and limitations of WiTricity, and envisions a future where wireless power could eliminate wires and batteries.