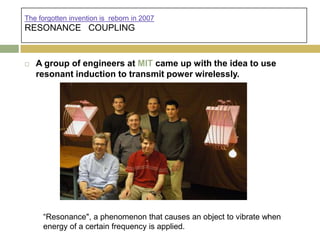
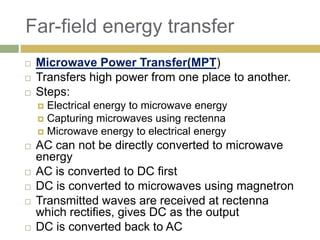
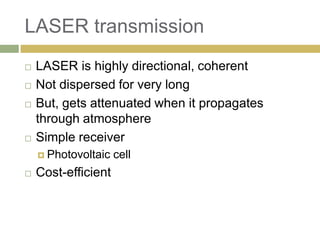
1) Wireless power transmission through resonance coupling was proposed by Nikola Tesla in 1899 and experiments were conducted at MIT to transmit power without wires over short distances.
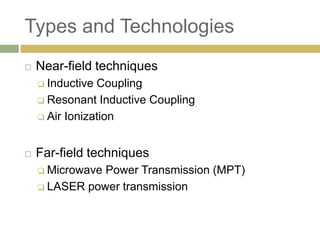
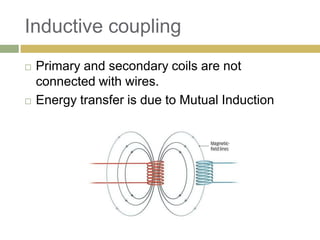
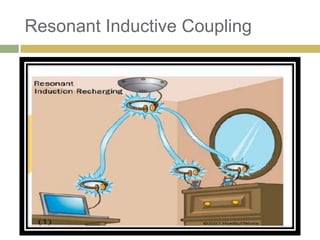
2) Witricity uses resonant inductive coupling to efficiently transfer power between two electromagnetic resonators over mid-range distances without power loss.
3) Applications of wireless power include powering consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and industrial/transportation systems without wires, helping reduce e-waste and installation costs.