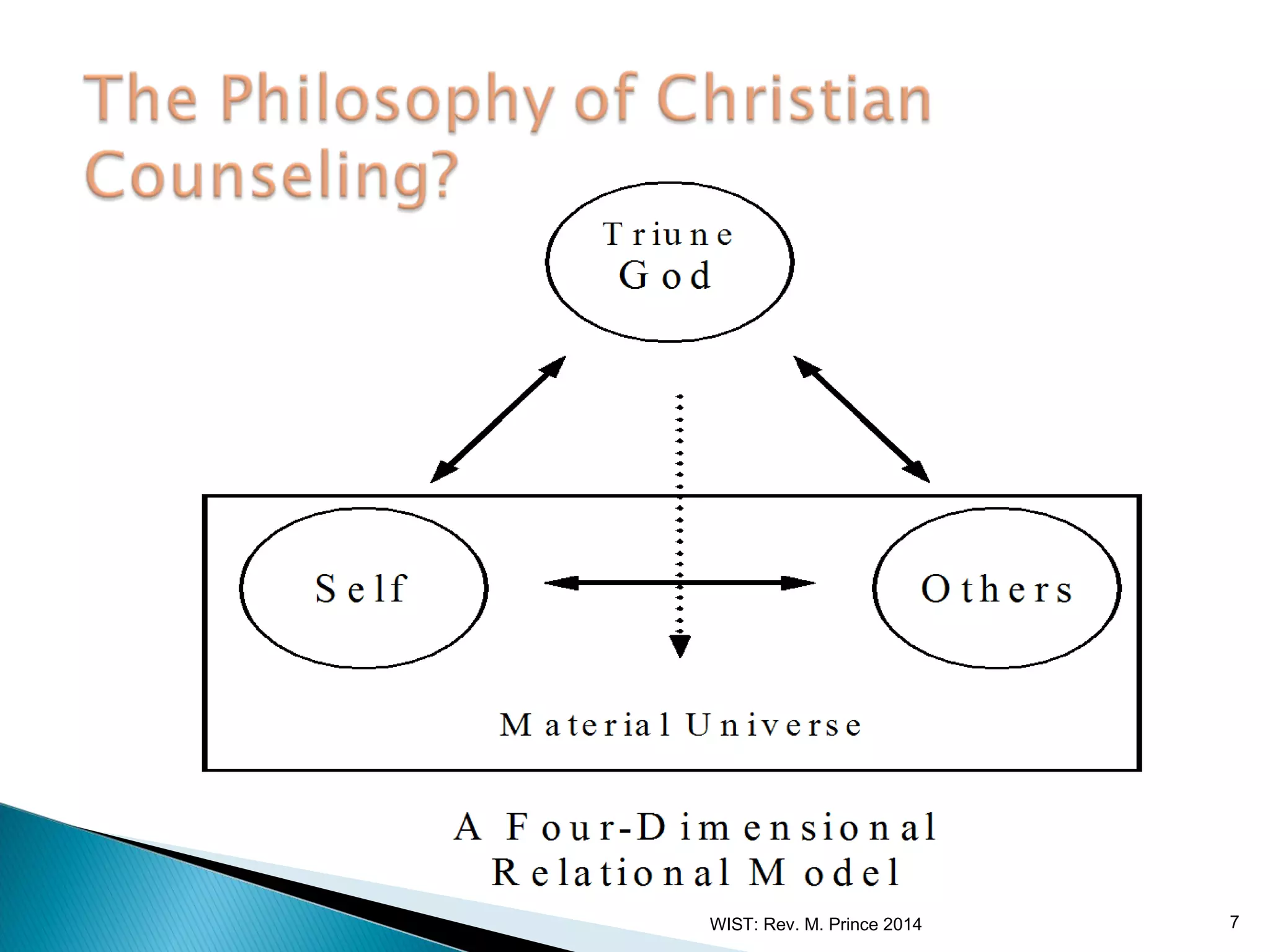
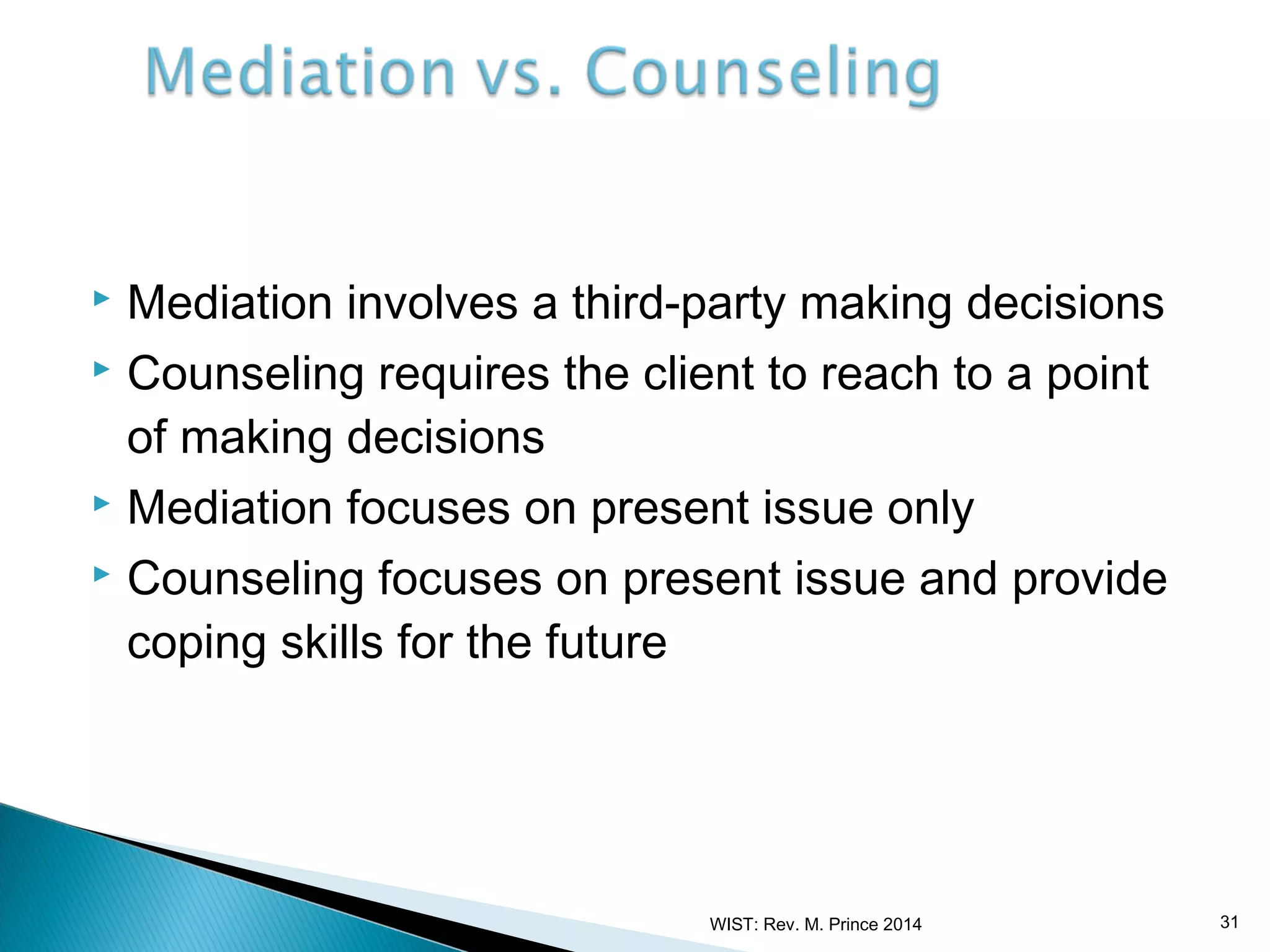
Counseling is defined as an applied social science that helps individuals better understand themselves and handle their roles and relationships effectively. It involves the application of mental health principles through cognitive, affective, behavioral or systematic interventions to encourage growth and help people cope with problems. Counseling aims to provide encouragement and guidance for those facing challenges. It is both a science, through the use of techniques and procedures for problem solving, and an art, through the counselor's unique experiences in assisting clients. Christian counseling specifically applies biblical principles to treat clients' issues using professional counseling methods.