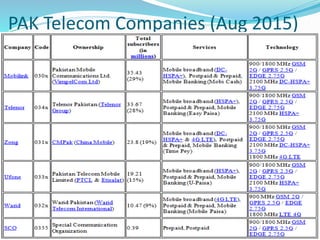
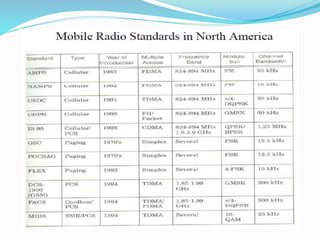
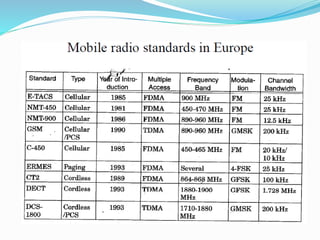
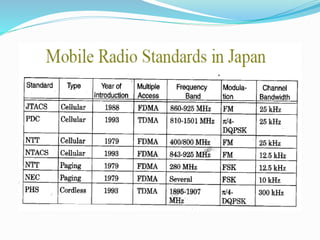
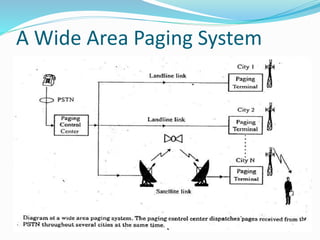
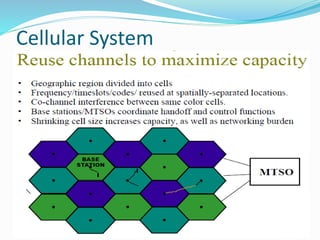
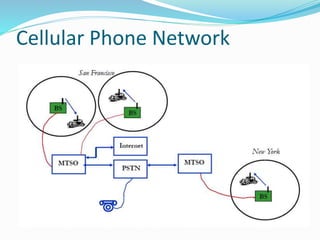
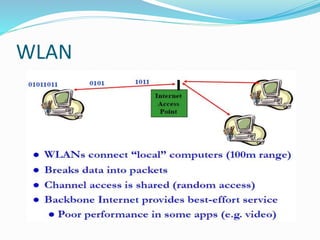
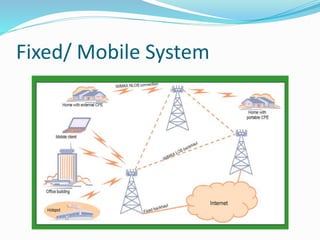
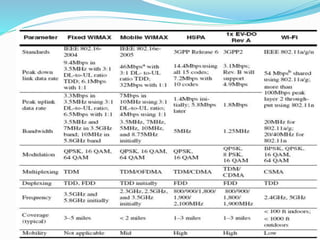
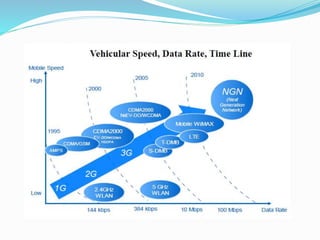
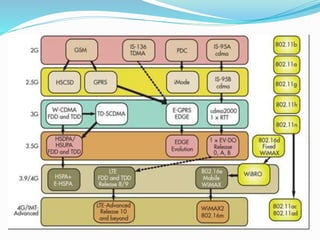
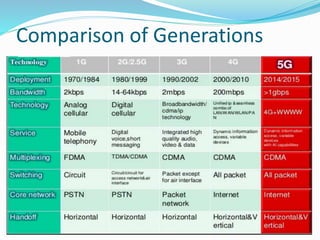
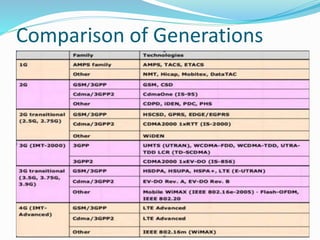
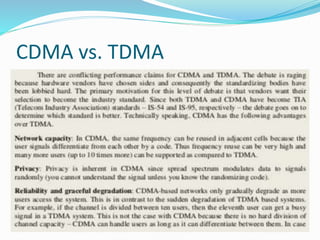
The document discusses various types of wireless communication technologies. It describes how wireless communication allows transmission of information through electromagnetic waves like radio frequency and infrared without wires. It provides details on different wireless technologies including satellite communication, infrared, microwave communication, WiFi, Bluetooth, mobile communication systems and more. It also discusses concepts like multiple access techniques, wireless standards and compares cellular communication generations.