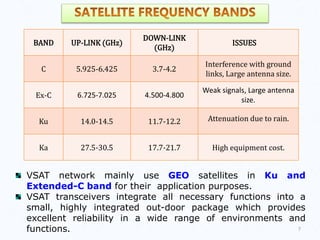
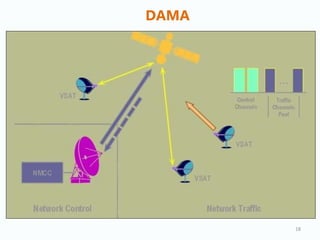
VSAT (Very Small Aperture Terminal) technology allows for wireless communication via satellite using small dish antennas. A VSAT network consists of a central hub with a large antenna that communicates with multiple remote VSAT sites. The hub controls and monitors the network, sending data to the satellite which amplifies and redirects the signals to the VSATs. VSAT offers advantages like flexibility, lower installation costs than terrestrial networks, and ability to access areas without terrestrial infrastructure. Common applications of VSAT include corporate networks, internet access, distance education, and retail/banking networks. VSAT uses multiple access techniques like TDMA to allow efficient sharing of satellite bandwidth among sites.




![TYPES OF SATELLITES
According to orbit position satellites are of mainly three
types:
LEO(Low Earth Orbit satellite )
MEO(Medium Earth Orbit satellite )
GEO(Geosynchronous Equatorial Orbit satellite )
6Ref:[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/43akshay-copy-140509103311-phpapp02/85/VSAT-Technology-6-320.jpg)





![VSAT HUB NETWORK
15
Ref:[4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/43akshay-copy-140509103311-phpapp02/85/VSAT-Technology-15-320.jpg)



![20
VARIOUS VSAT PRODUCTS
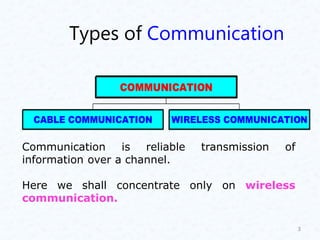
Comparison of various VSAT Network Characteristics
Supplier Hardware Type Inbound Data
Rate (kb/s)
Outbound Data
Rate (kb/s)
Modulation
Gilat/Spacenet Skystar
Advantage
TDM/TDMA 9.6, 19.2, 38.4,
56, 64, 76.8,
128
64, 128, 256,
512, 1024, 2048
DPSK or MSK
Hughes ISBN/PES TDM/TDMA 64, 128, 256 128, 512 BPSK
Indra Espacio Arcanet CDMA
NEC Nextar V TDM/TDMA 64, 128, 256 64, 128, 256,
512, 768, 1536,
2048
BPSK/QPSK
STM X.Star TDM/TDMA 96, 192, 384 64, 128, 256,
512, 1024, 1544
BPSK
TSAT TSAT 2000 TDM/TDMA 0.3, 0.6, 1.2,
2.4, 4.8
0.3, 0.6, 1.2,
2.4, 4.8
4FSK, 2-
4PSK
TSAT TSAT 2100 TDM/TDMA 2.4 - 9.6, 14.4,
16.8
2.4 - 9.6, 14.4,
16.8
QPSK
ViaSat Sky Relay TDM/TDMA
Ref:[4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/43akshay-copy-140509103311-phpapp02/85/VSAT-Technology-20-320.jpg)


![23
REFERENCES
[1] Ha, Tri T., Digital Satellite Communications, 2nd ed., TMH,
2009.
[2]http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Very-small-aperture_terminal
[accessed on 25/09/2013].
[3]http://www.cse.iitb.ac.in/synerg/lib/exe/fetch.php?id=public%
3astudents%3azahirk%3adm%3ainterfacing_to_pc&cache=cach
e&media=public:students:zahirk:dm:vsat_doc.pdf [accessed on
29/10/2013]
[4] http://novastars.com/vsat [accessed on 28/10/2013].
[5] Rao, K.N. Raja, Fundamentals of satellite communication,
PHI pvt. Ltd., 2004.
[6] Tseng, Yuh M., Cryptanalysis and Improvement of Key
Distribution System for VSAT Satellite Communications,
INFORMATICA, 2002, Vol. 13, No. 3, P 369–376.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/43akshay-copy-140509103311-phpapp02/85/VSAT-Technology-23-320.jpg)
