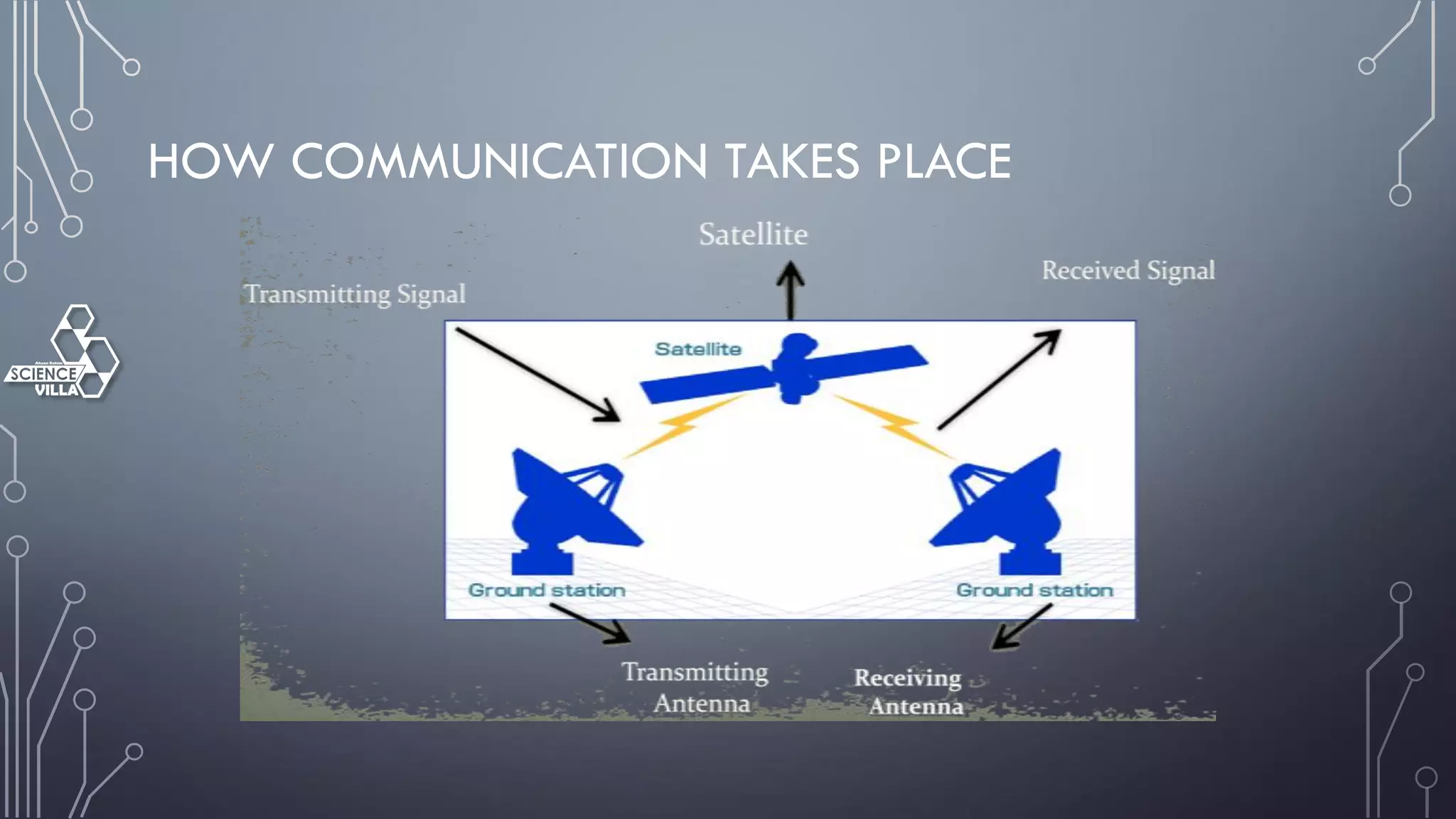
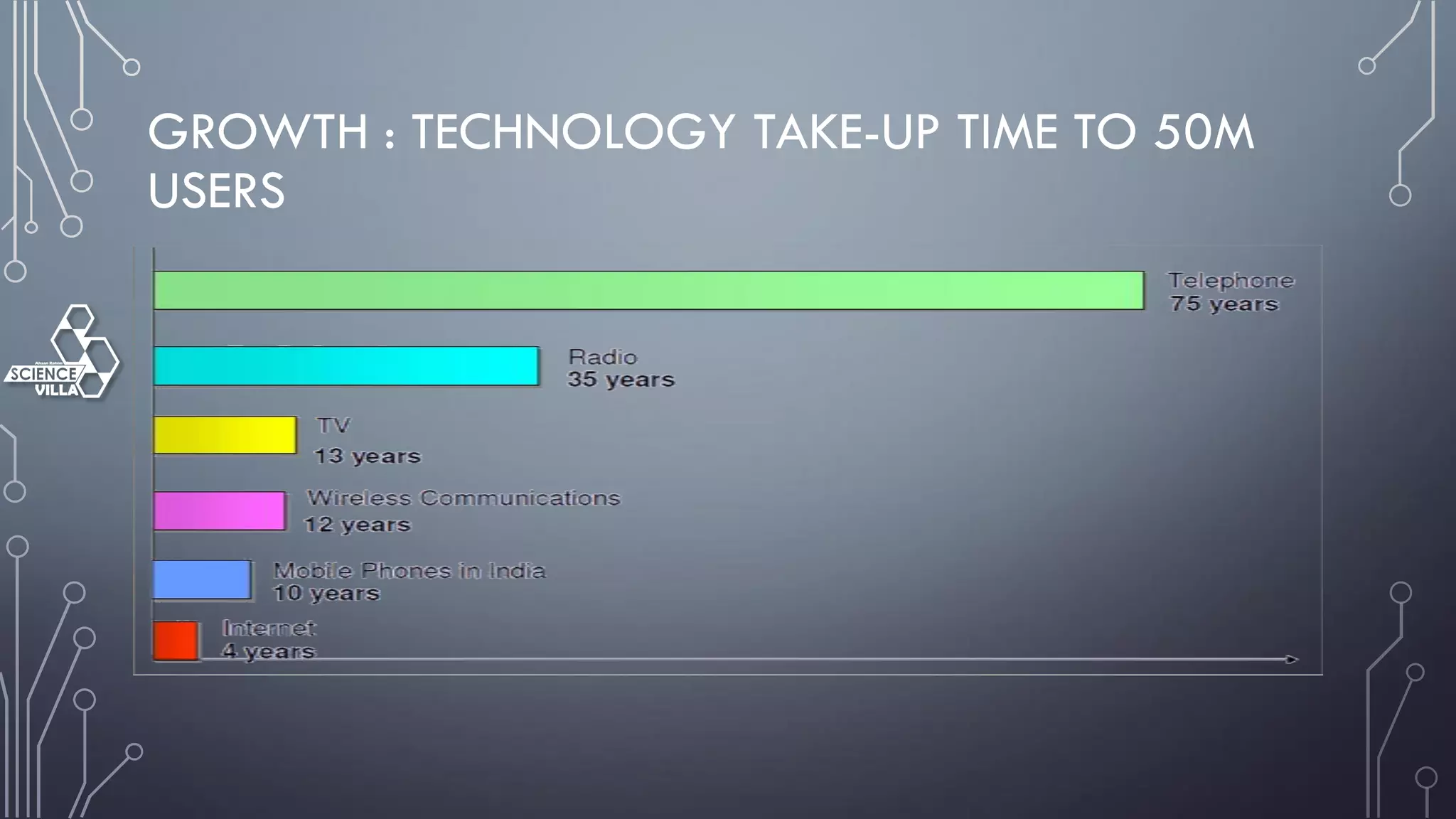
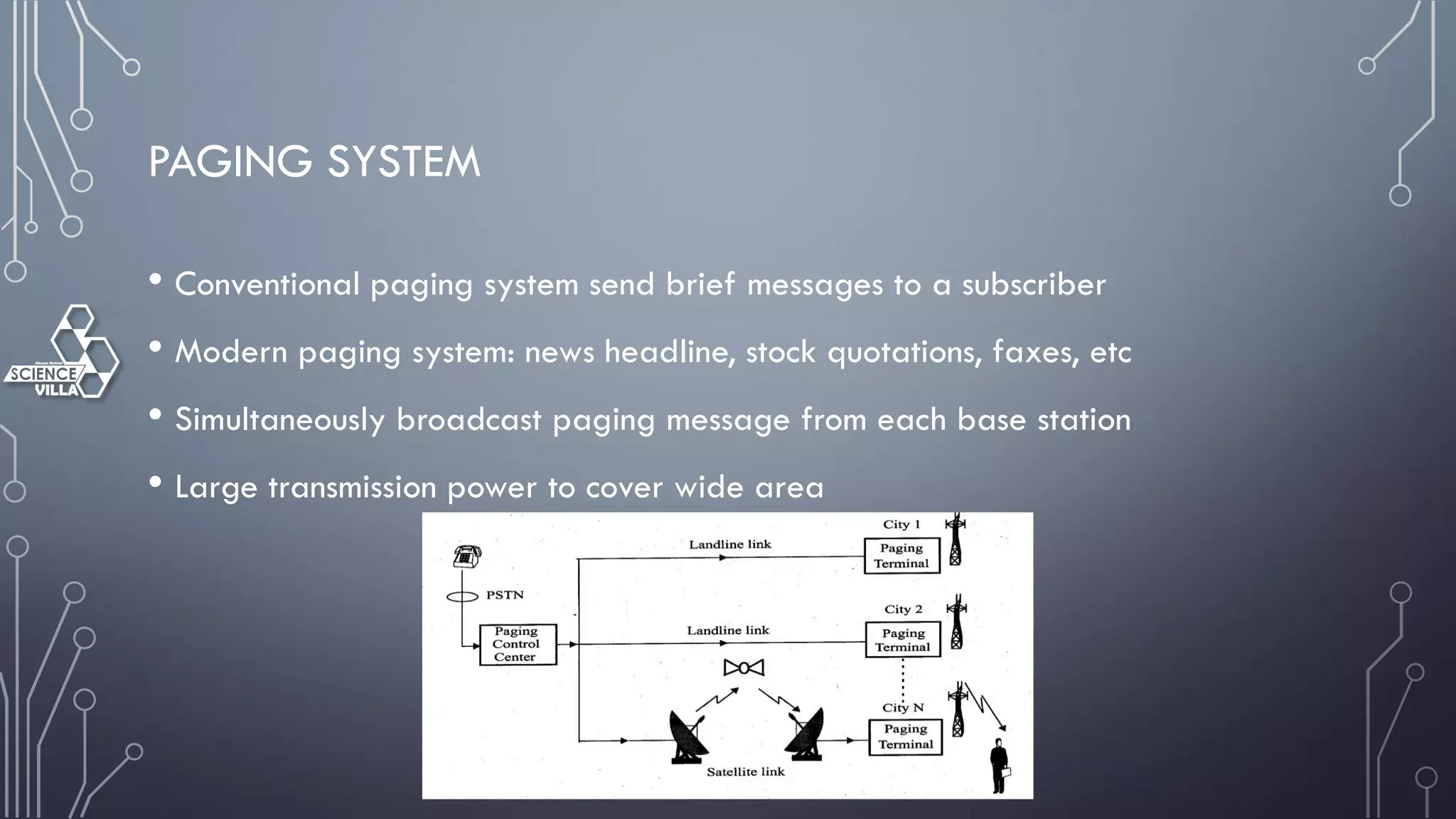
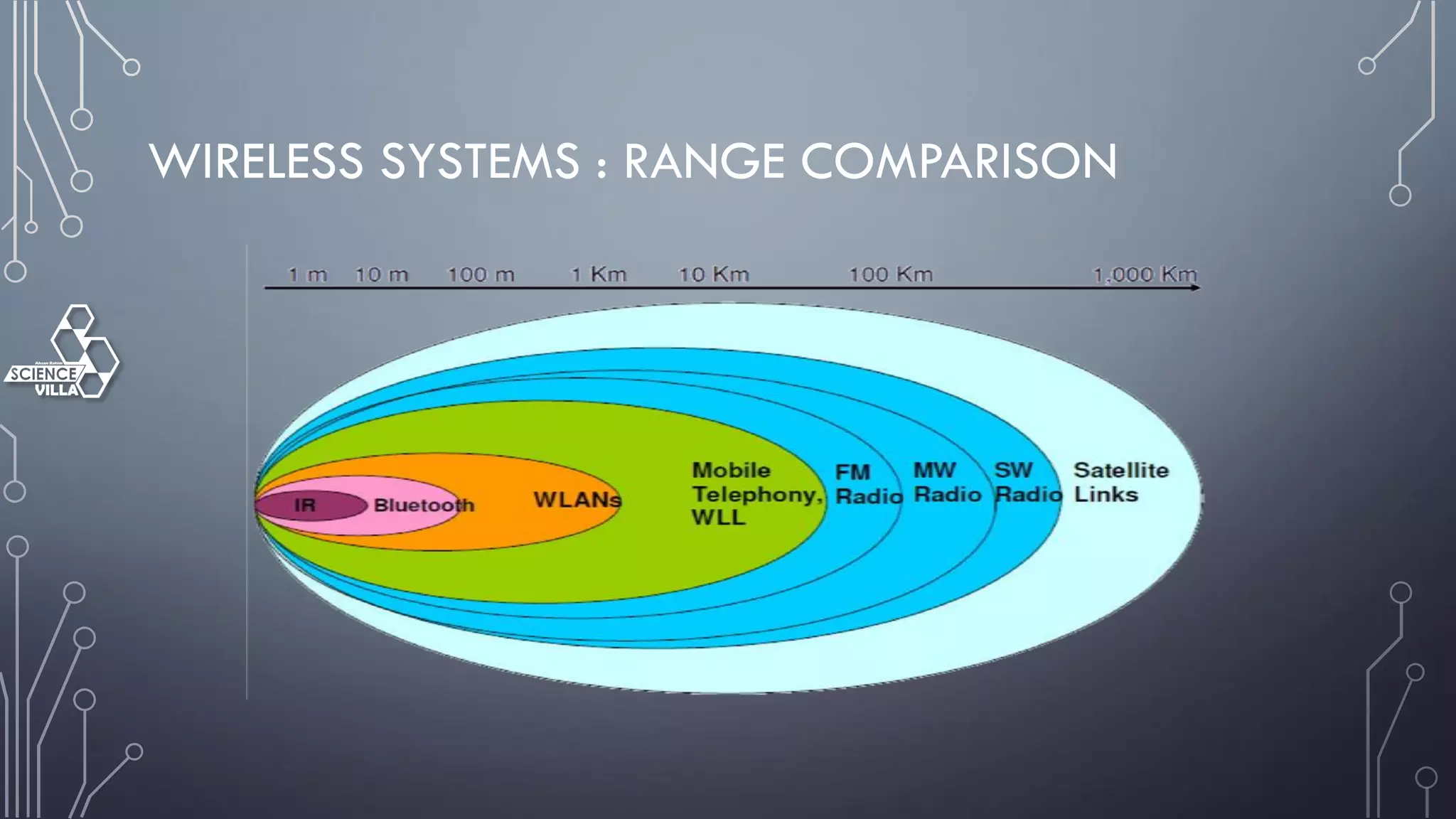
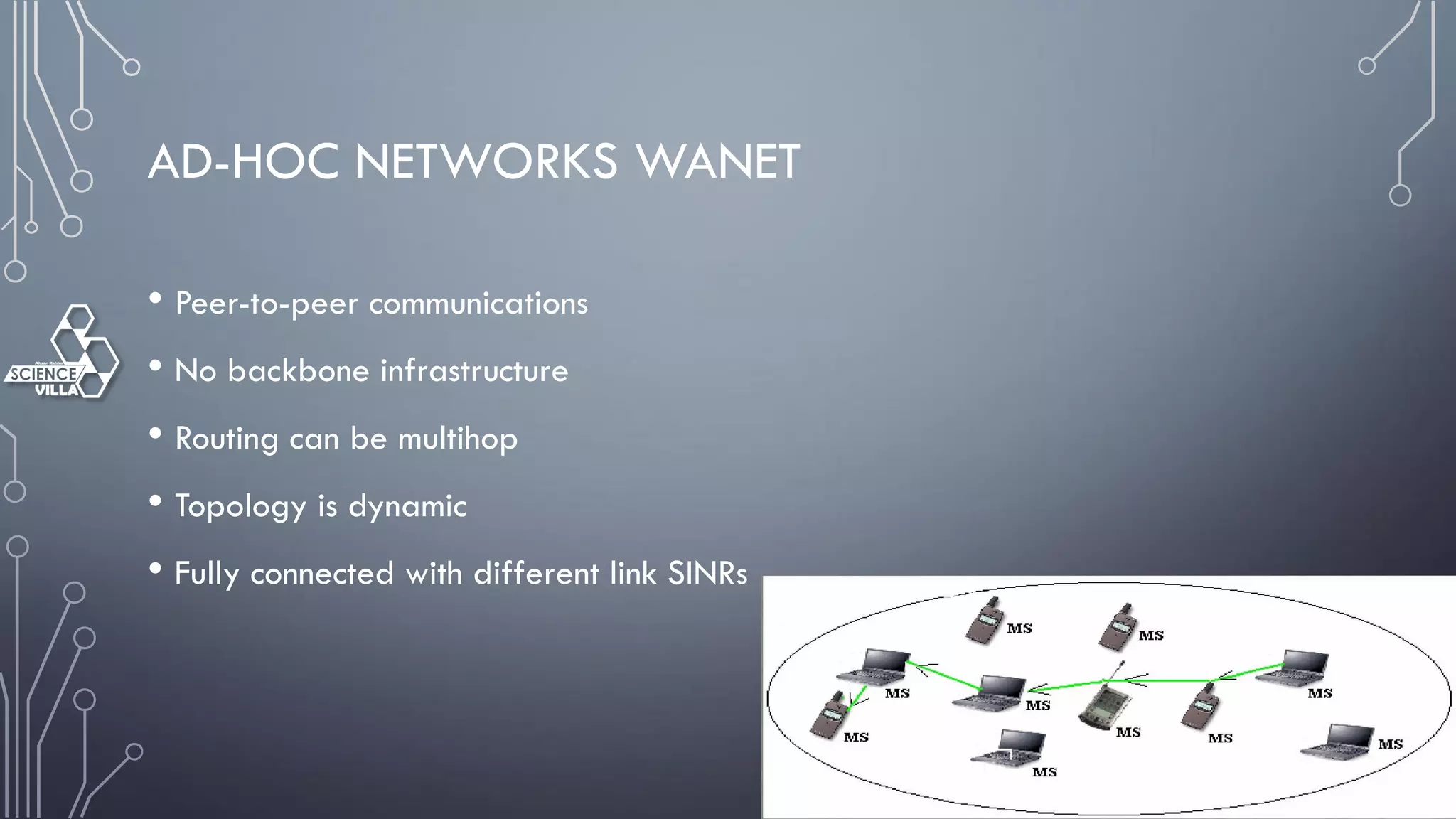
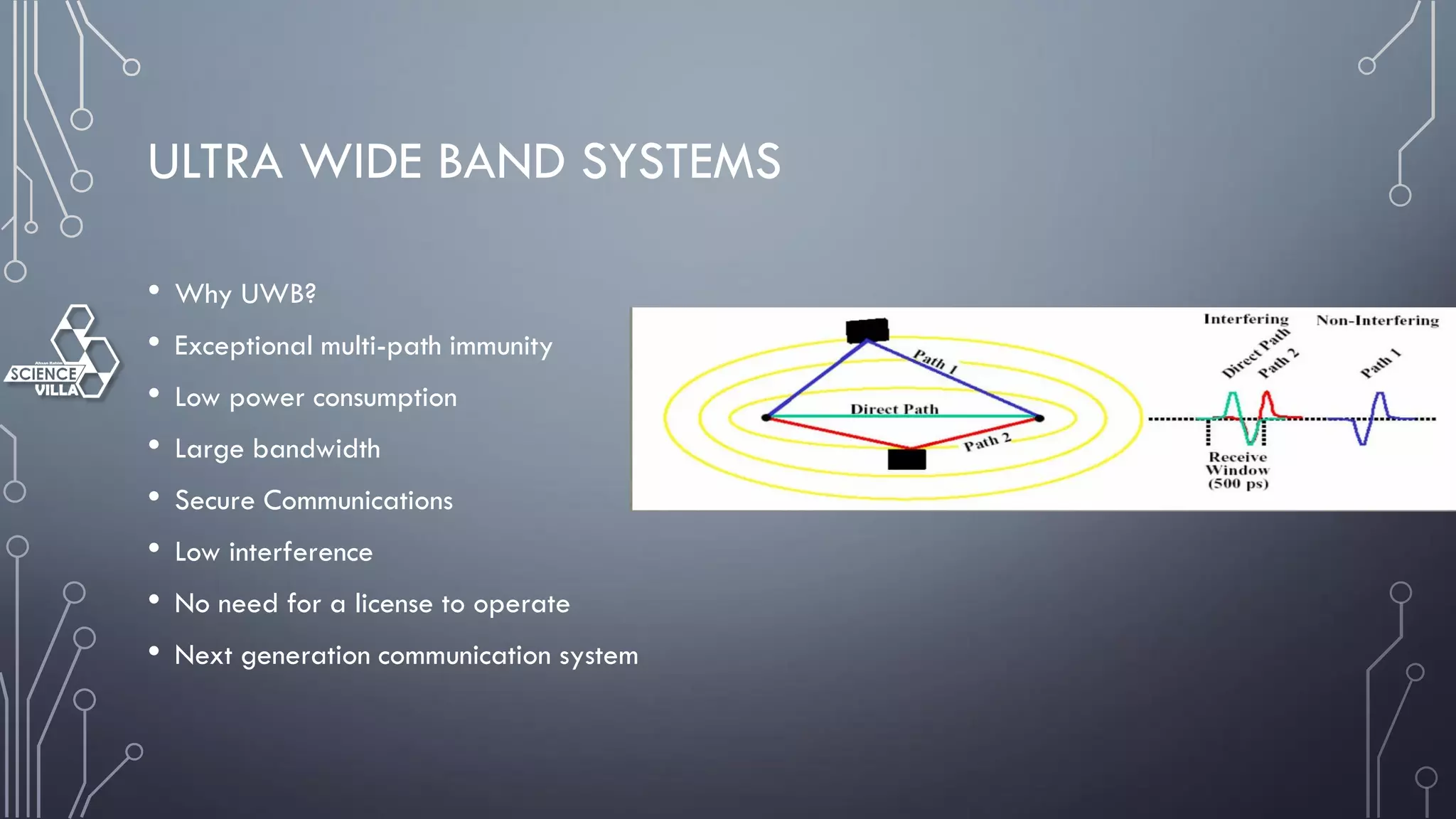
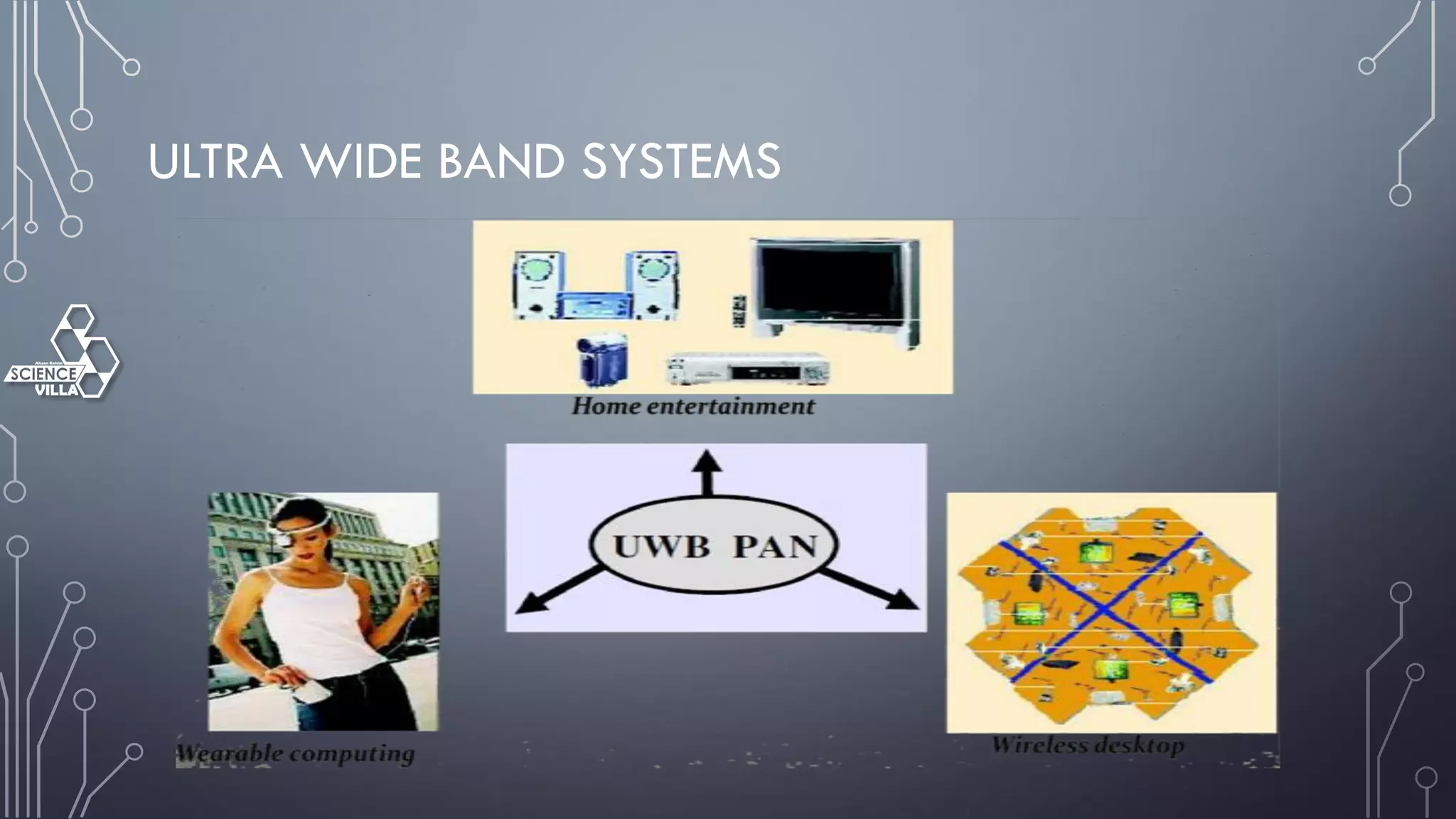
Wireless communication is the transfer of information between points without wires, using electromagnetic waves over defined channels. It offers benefits like mobility and cost savings but faces challenges such as security vulnerabilities and interference. Various wireless systems include cellular, satellite, and Bluetooth, each with distinct characteristics and applications.