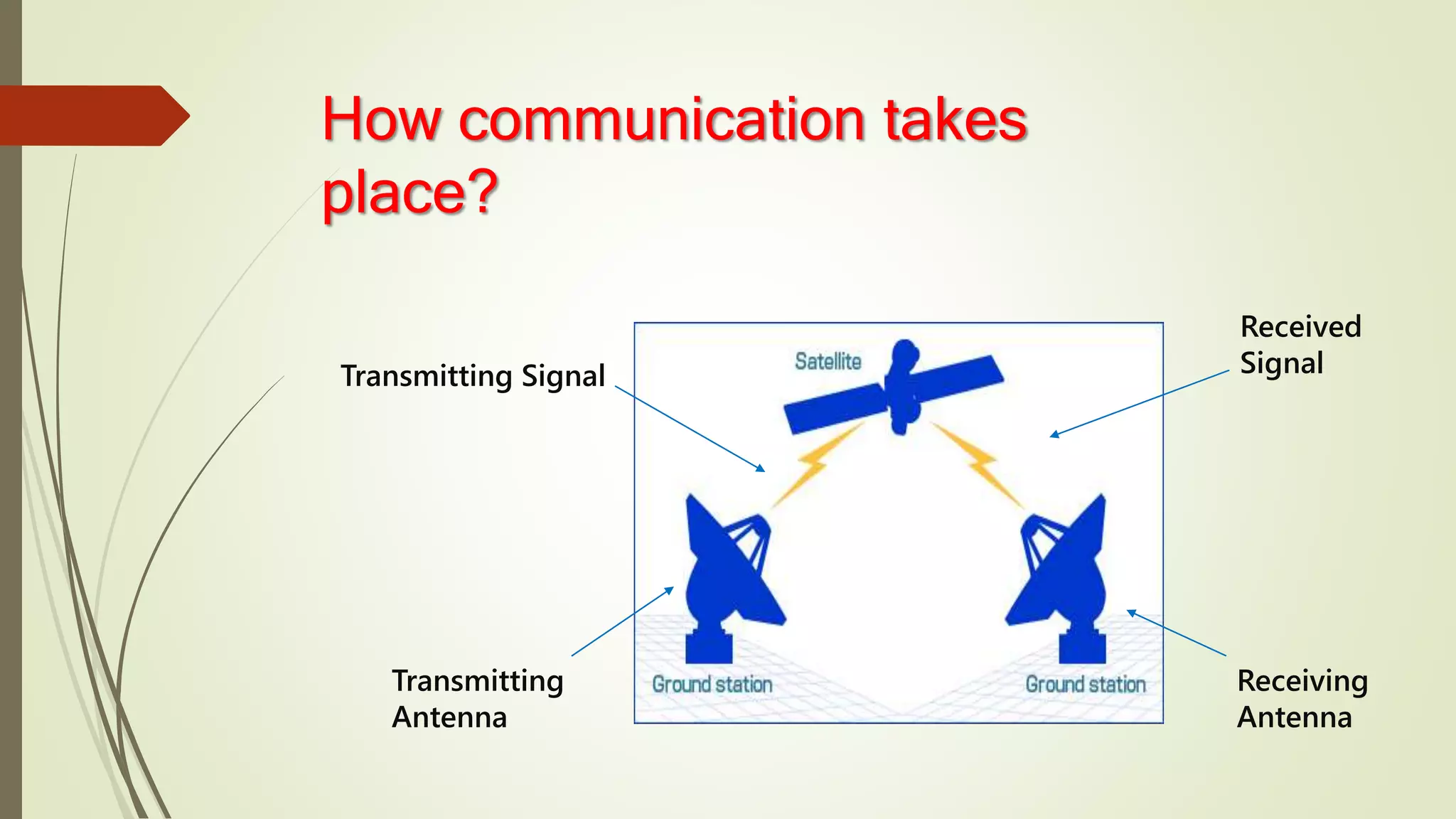
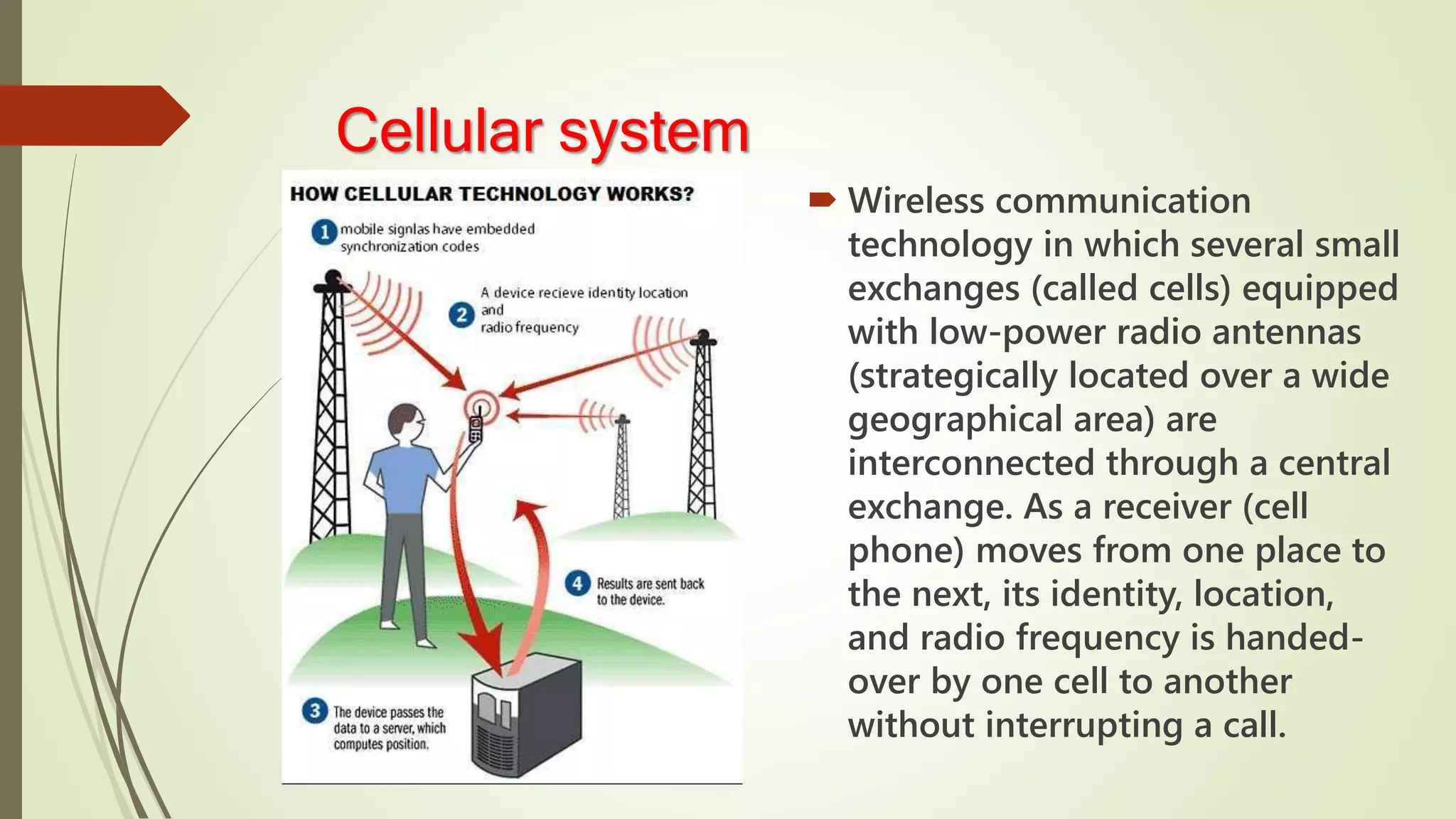
This document discusses various aspects of wireless communication. It begins by explaining the benefits of wireless communication such as freedom from wires and global coverage. It then describes how wireless communication works by transmitting electromagnetic waves between a transmitting and receiving antenna. It provides examples of typical frequency bands used for different wireless technologies like FM radio, TV, and WiFi. The document goes on to explain key concepts such as channels and discusses different types of wireless transmission including radio, microwave, infrared and light waves. It also outlines current wireless systems including cellular networks, wireless LANs, satellite systems, personal area networks and paging systems.