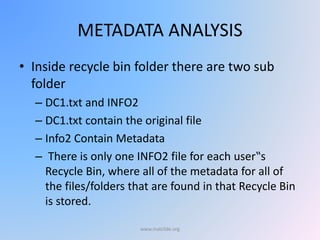
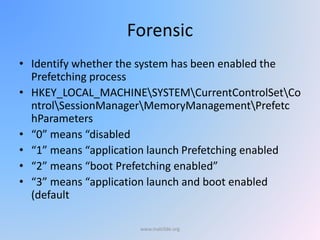
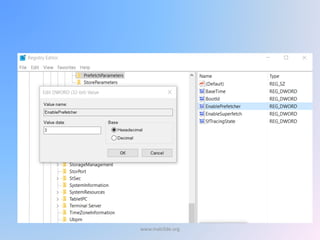
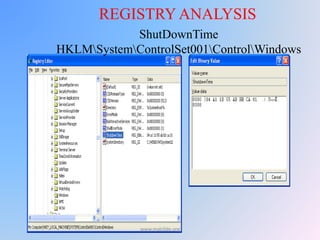
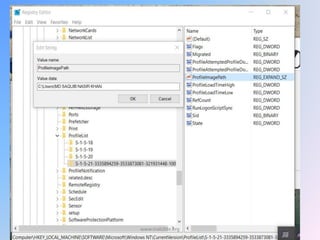
The document provides an overview of Windows forensic techniques for gathering digital evidence across various versions of the Windows operating system. It discusses key areas such as recycle bin forensics, registry analysis, and the importance of files like hiberfil.sys, paging files, and thumbs.db for forensic investigations. The document emphasizes the significance of metadata and system settings in understanding user actions and system behavior.





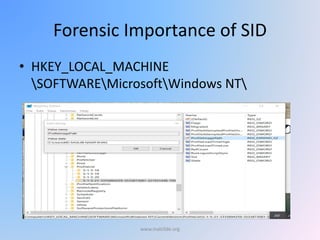
![Every file sent to the recycle bin is renamed in the following
format
D[ orginal drive letter of file][index no][original extension]
E.g. hw1.txt residing in C:My Documents was sent to empty
recycle bin
» Its new name is DC0.txt
www.malc0de.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/windowsforensic-160630095552/85/Windows-forensic-6-320.jpg)