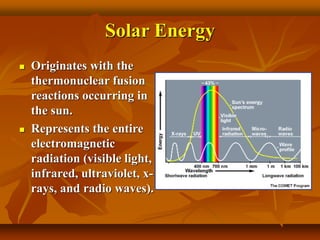
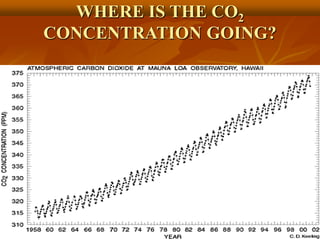
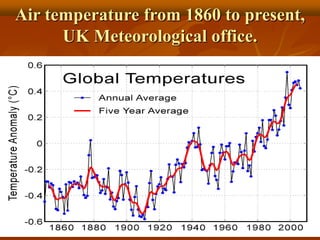
The document discusses renewable and non-renewable energy sources, highlighting that renewable energy is generated from natural and abundant sources like the sun, wind, and tides, whereas non-renewable energy comes from limited sources like fossil fuels that will eventually deplete. It emphasizes the environmental benefits of renewable energy, including lower carbon emissions and the necessity to manage non-renewable resources carefully due to their harmful effects on health and the climate. The text also explains various methods of energy generation, including solar, wind, and tidal energy, and their mechanisms.