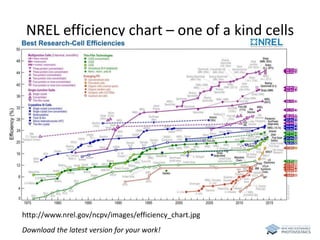
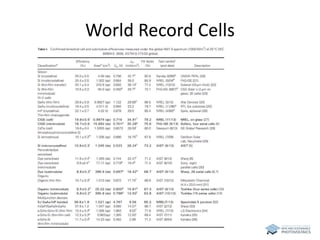
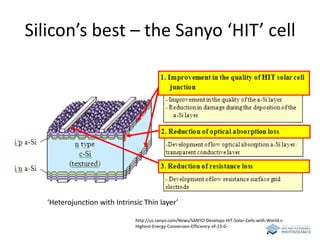
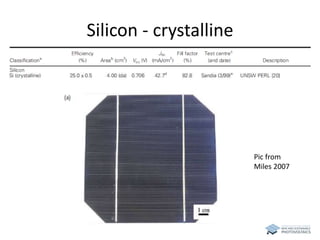
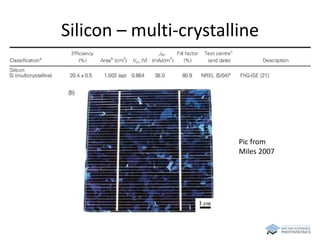
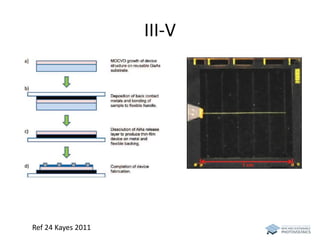
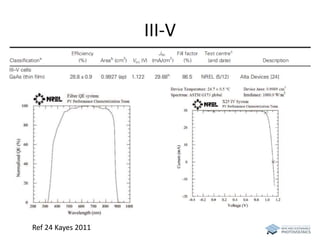
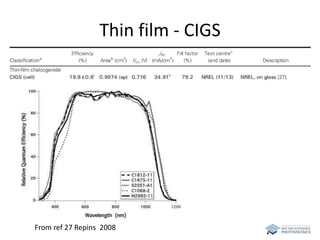
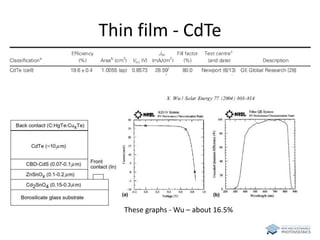
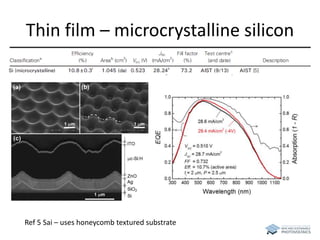
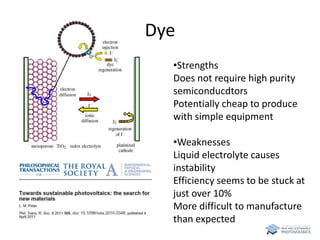
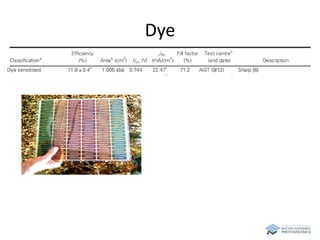
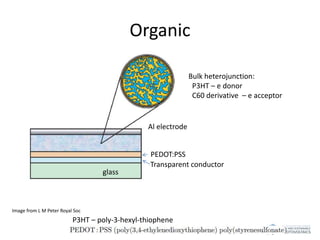
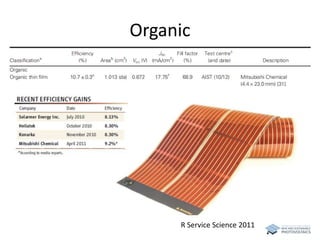
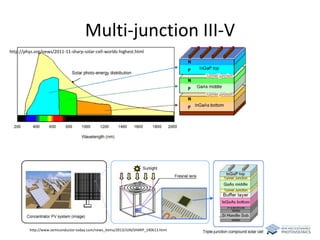
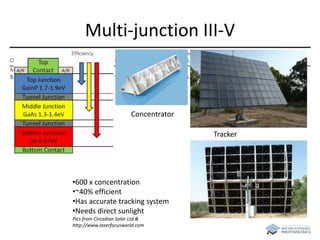
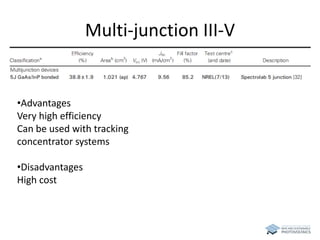
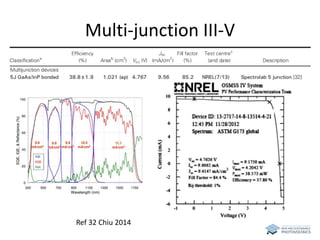
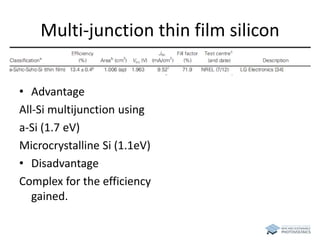
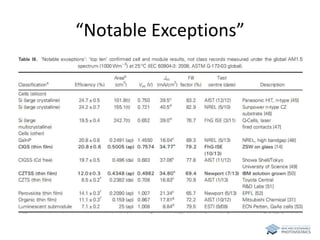
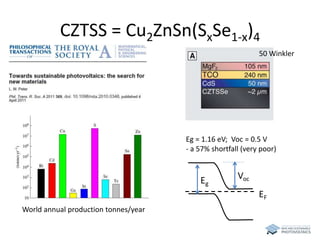
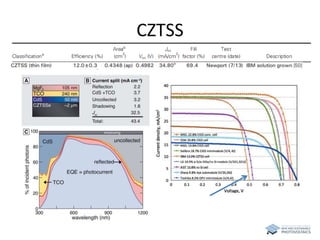
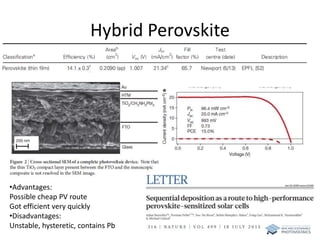
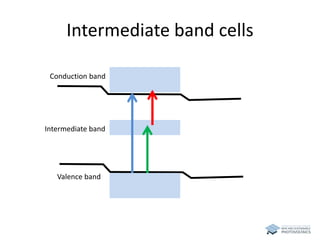
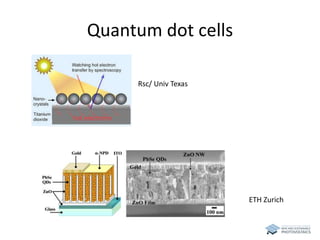
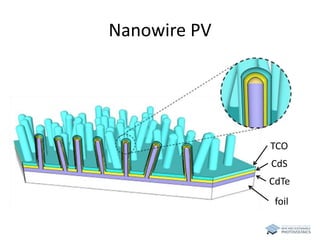
The document discusses various solar cell technologies, including their world record efficiencies. It covers traditional silicon technologies, as well as thin-film technologies like CIGS and CdTe. Emerging technologies discussed include perovskites, dyes, organics, and multi-junction cells. For each technology, it provides the strengths and weaknesses, example efficiency levels, and sometimes a diagram. It aims to give an overview of both established and new concepts in photovoltaics.