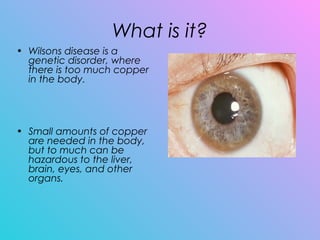
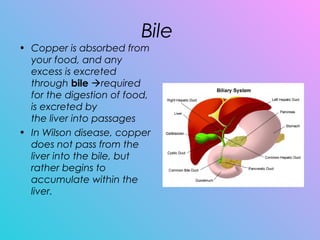
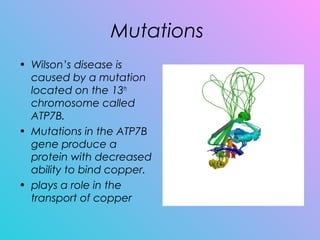
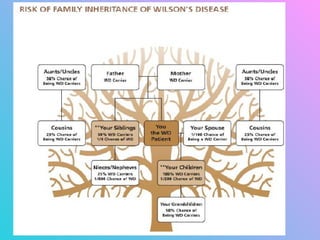
Wilson's disease is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation on the ATP7B gene that results in too much copper being absorbed and retained in the body's organs like the liver and brain. It is typically diagnosed through tests measuring copper levels in the blood and liver tissue. Lifelong treatment focuses on removing excess copper through medication or transplant and preventing further copper absorption through diet.