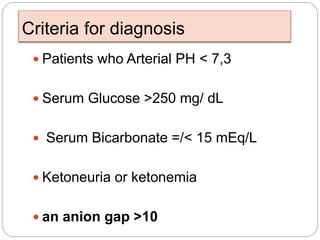
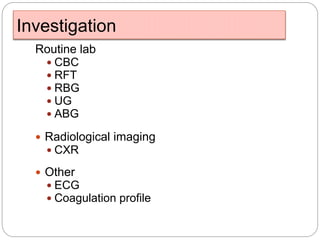
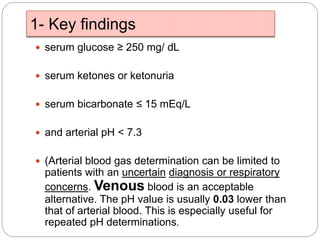
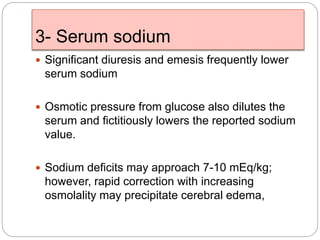
1. The document discusses disorders of carbohydrate metabolism, focusing on diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS).
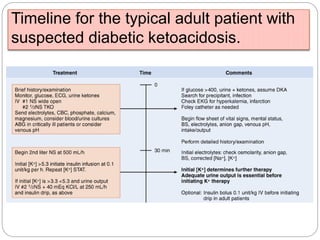
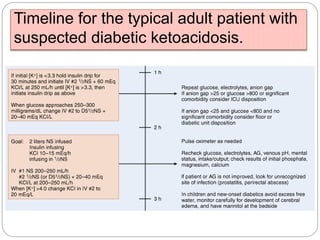
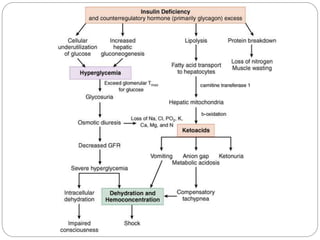
2. DKA is characterized by high blood glucose, low pH, and ketones in the blood or urine. HHS involves extremely high blood glucose without acidosis or significant ketones.
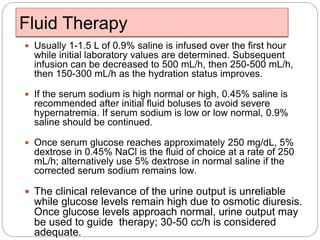
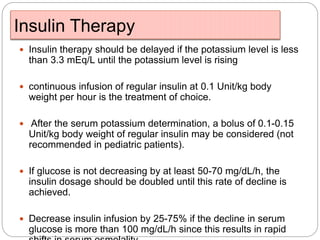
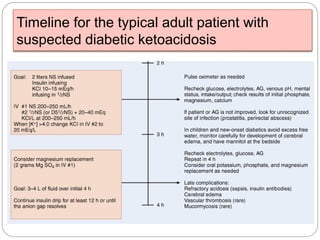
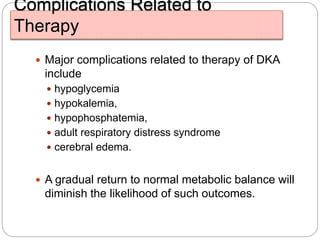
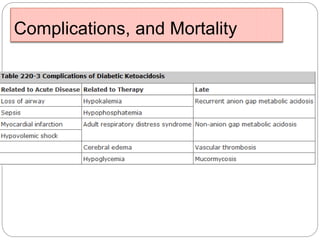
3. Treatment for both involves fluid resuscitation, insulin administration, electrolyte replacement, and monitoring for complications. Careful attention must be paid to fluid balance, electrolyte levels, and glucose control during resuscitation.











![5- Other important laboratory
findings
A.Anion Gab
useful to assess severity of acidosis and to follow
progress of therapy
Anion Gab = [Na]- [Cl] + [HCO3]
Normal values are 8- 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metabolicendocrineemergencies2-190805173147/85/Metabolic-amp-endocrine-emergencies-2-17-320.jpg)
![5- Other important laboratory
findings
B- serum osmolality:
= 1.86[Na]+(glucose/18)+(BUN/2.8)
osmolality values above 340 mOsm/kg usually result in
mental status changes.
Below this value, other causes for lethargy or coma
should be investigated.
This value may also be used to diagnose hyperosmolar
hyperglycemic state (HHS) and ingestions of ethanol,
ethylene glycol, or other alcohols.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metabolicendocrineemergencies2-190805173147/85/Metabolic-amp-endocrine-emergencies-2-18-320.jpg)