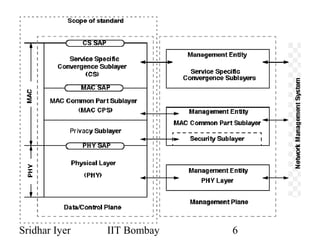
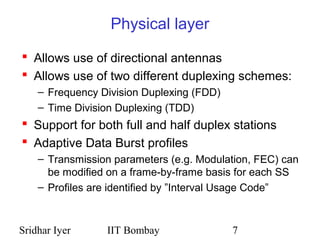
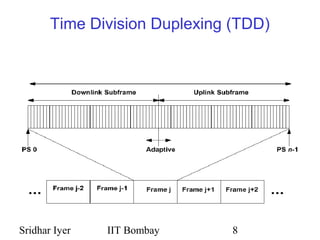
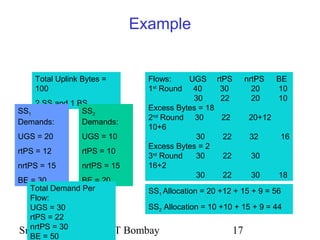
WiMAX (IEEE 802.16) provides wireless broadband access over long distances using base stations. It supports quality of service for applications and allows centralized control of subscriber stations to prevent collisions. The physical layer allows directional antennas and uses frequency or time duplexing. The media access control layer uses maps to define uplink and downlink bursts and manages connections through identifiers. Bandwidth is allocated to subscriber stations based on requests using different service types like unsolicited grants or real-time polling.