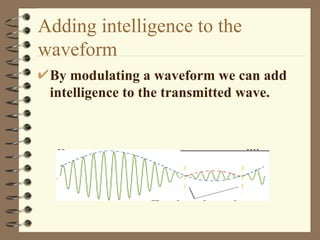
A carrier signal is a frequency that is modulated to carry analog or digital information for communication. Common examples are radio transmitters that modulate the frequency or amplitude of a carrier signal to transmit audio information. A carrier system provides multiple point-to-point communication channels using a technique like time-division multiplexing. Carrier service providers offer telephone and data communication between locations using networks like those built by Regional Bell Operating Companies. Modulation involves impressing voice, music, pictures or data onto a radio frequency carrier wave by varying its amplitude, frequency or phase. Common modulation types include amplitude modulation, frequency modulation, phase modulation, pulse code modulation and pulse duration modulation.