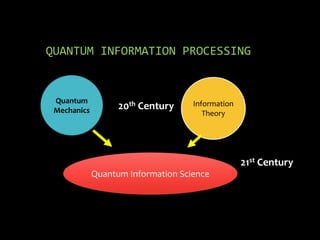
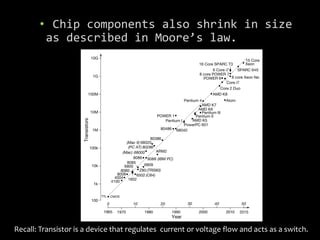
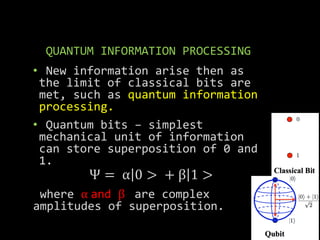
The document explores the relationship between quantum computers and quantum mechanics, emphasizing quantum information processing, quantum entanglement, and advancements in quantum computer hardware. It discusses the implications of miniaturization in technology and the potential outcomes of developing large-scale quantum computers or uncovering limitations in quantum mechanics. Key concepts like superposition, the role of quantum bits, and the need for high quantum efficiency measurements are highlighted.