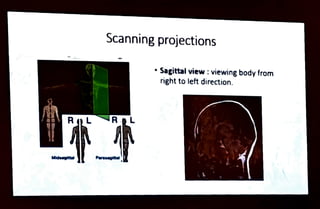
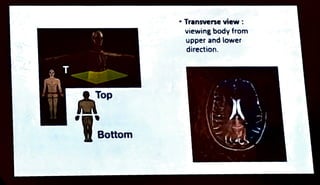
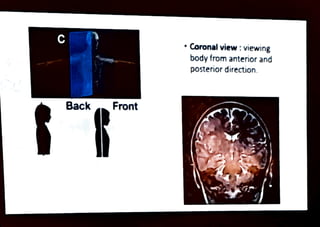
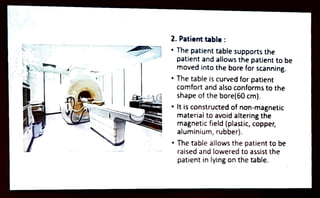
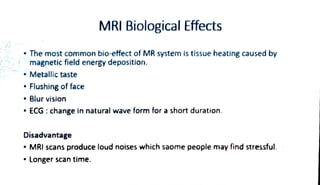
MRI is a diagnostic imaging technique that utilizes the magnetic properties of hydrogen protons in the human body, which is predominantly composed of water. It involves equipment such as a gantry, patient table, and computer to create images viewed in different orientations. Important safety considerations must be taken into account, including the presence of metallic implants and other contraindications.