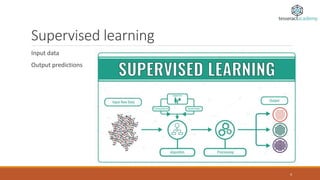
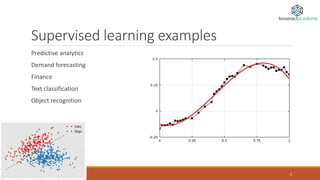
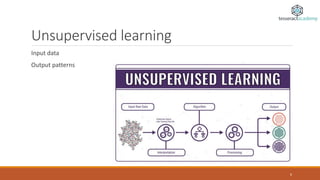
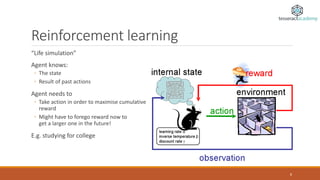
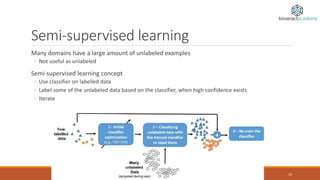
The document provides an overview of machine learning, defining it as the ability of computers to learn from data without explicit programming. It outlines different types of machine learning, including supervised, unsupervised, reinforcement, semi-supervised, and active learning, along with examples and applications for each. It also highlights the importance of big data in the success of machine learning and provides resources for further learning.

![What is machine learning?
Arthur Samuel (1959): ”Machine learning is about giving computers the ability to learn without
being explicitly programmed."[1]
Bottom-up approach
◦ Data-driven
◦ Use a learning algorithm that extracts patterns from data
◦ Opposite of classic-AI (handcrafted rules)
No direct control
◦ Choice of algorithm (but not much else)
◦ Parameters of the algorithm
◦ Not possible to include explicit rules or directly affect the outcome
Most successful field of AI
◦ Facilitated by the big data explosion
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatisml-181006091433/85/What-is-ml-2-320.jpg)