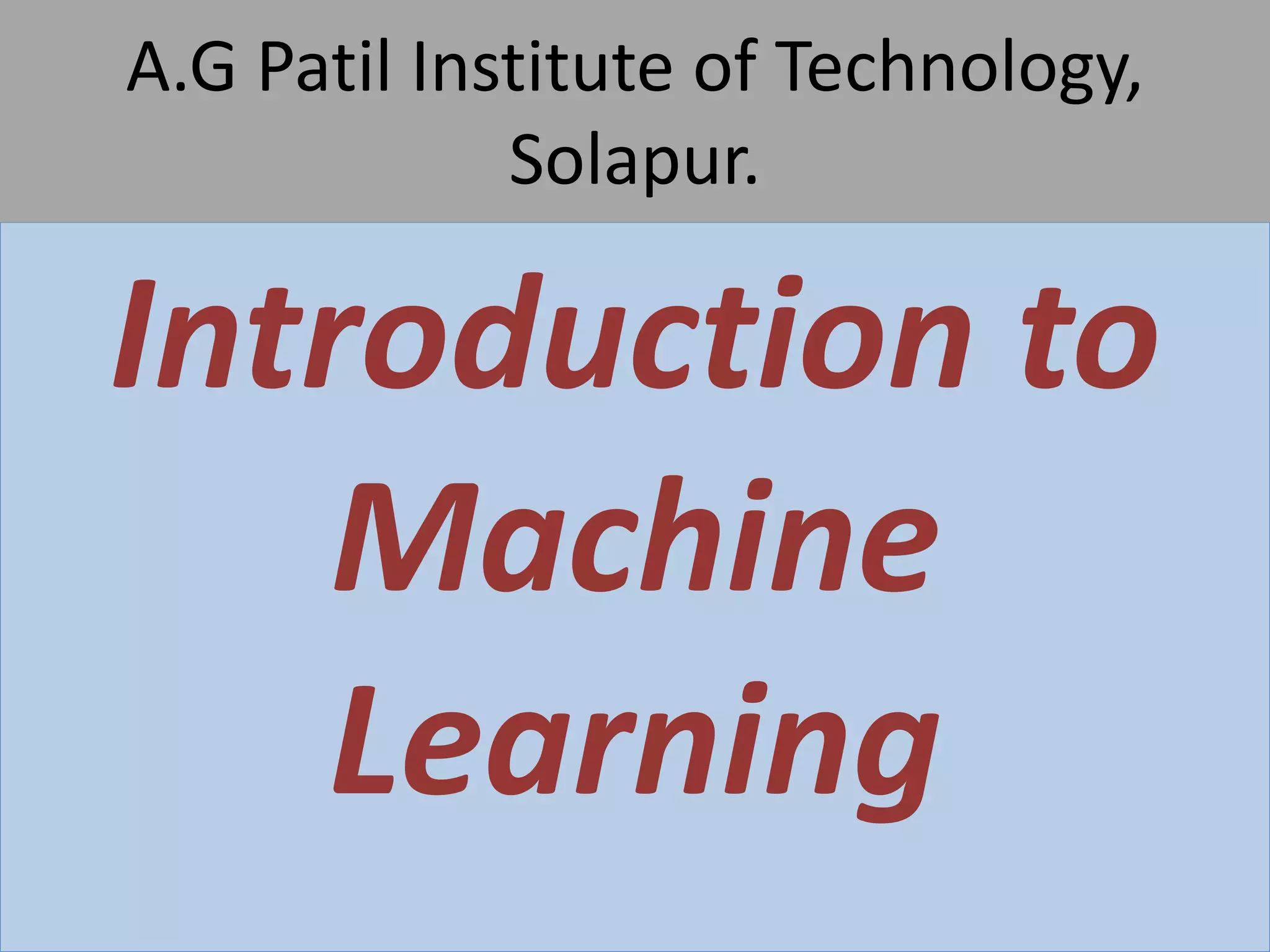
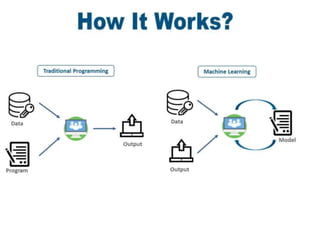
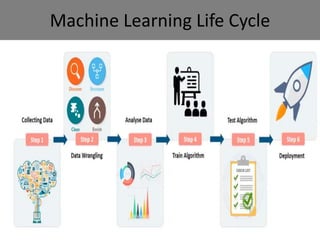
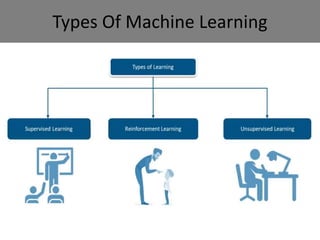
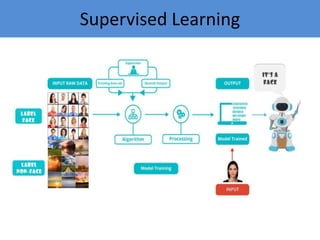
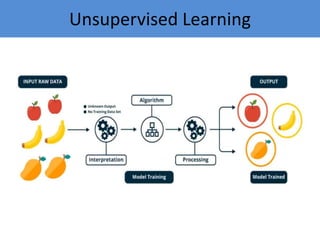
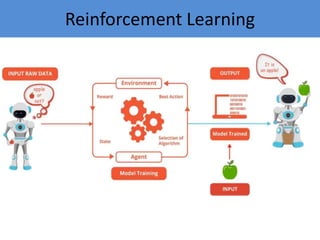
The document provides an introduction to machine learning, covering its definition, types (supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning), and applications. It emphasizes that machine learning enables computers to learn from data and improve performance without explicit programming. Additionally, it outlines the machine learning life cycle and various real-world applications such as virtual assistants, marketing, and computer vision.